WORKBOOK ANSWERS OCR GCSE (9-1) PE - Workbook Papers 1 and 2 - Hodder Education
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
WORKBOOK ANSWERS
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE
Workbook
Papers 1 and 2
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
Paper 1: Physical factors
affecting performance
Topic 1 Applied anatomy
and physiology
The structure and functions of the skeletal system
Practice questions (page 5)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1
2 Bone marrow in some larger bones
3
Heart = Ribs
Brain = Cranium
Spinal cord = Vertebrae
2
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
4 Iron: transports oxygen to the working muscles / Calcium: builds and repairs bones
5 Freely moveable/allows movement
6
Joint Type
Knee Hinge
Hip Ball and socket
Shoulder Ball and socket
Elbow Hinge
7 A- Scapula
8 Rotation and circumduction
9 A- they connect bone to muscle
10 One mark from:
• Reduce friction
• Act as a shock absorber for the joint
AO2: Application
11 Femur and tibia
12 One mark from:
• Humerus
• Radius
• Ulna
13 Shin pads
14 Abduction
3
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
15
Knee: extension
Ankle: plantarflexion
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
16
Support: Keeps the body upright/provides a framework to support the muscles when
playing.
Protection: In a tackle the ribs protect the heart/cranium protects the brain.
17 Any two from:
• They stabilise the joints as the tennis player moves around the court/prevent dislocation.
• They protect the joints/bones as they act as shock absorbers as the player runs and jumps.
• They help maintain correct posture/movement or enable proprioception.
The structure and functions of the muscular system
Practice questions (page 9)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1
4
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
2
Name of muscle Movement it performs
Pectorals Brings the arm back in towards the mid-line of the body (adduction at
the shoulder) and lifts the arm forwards (flexion at the shoulder joint)
Quadriceps Straightens the leg (extension of the knee joint))
Hamstrings Bends the leg (flexion of the knee joint)
Deltoid Lifts the arm forwards (flexion at the shoulder) and out to the side
(abduction of the shoulder)
Abdominals Bends the body forwards at the hips (flexion of vertebral column)
Gluteals Moves the leg backwards (extension of the hip joint) and brings the leg
back in towards the mid line of the body (adduction of the hip joint)
Biceps Bends the arm (flexion of the elbow)
Trapezius Extension at the neck
Gastrocnemius Points the toes (plantarflexion of the ankle)
Triceps Straightens the arm (extension of the elbow)
Latissimus dorsi Moves the arm backwards (extension of the shoulder joint) and brings
the arm back in towards the mid-line of the body (adduction of the
shoulder joint)
3 One mark for each correct answer.
5
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
4
Extension of the knee: quadriceps
Plantarflexion of the ankle: gastrocnemius
5 Latissimus dorsi
6 Triceps
7
Ankle joint: gastrocnemius
Knee joint: quadriceps
Hip joint: gluteals
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
8
• These muscles work as an antagonistic pair/antagonistically.
• Biceps contract and are the agonist.
• Triceps relax and are the antagonist.
Movement analysis
Practice questions (page 12)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1 Lever arm, pivot, effort, load
2
• First class lever
• Second class lever
• Third class lever
3 B- Moves a large load with a smaller effort
6
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
AO2: Application
4 One mark for each correct answer.
5 One mark for each blank filled in correctly.
The frontal plane runs vertically and divides the body into front and back sections.
Movements in this plane are sideways movements of abduction and adduction. The
transverse plane divides the body into upper and lower sections. Movements in this plane
are rotational. The sagittal plane splits the body vertically into left and right sides.
Movements in this plane are the up and down movements of flexion and extension.
6 One mark for each correctly labelled joint movement.
• Picture 1 (left): (hip) abduction
• Picture 2 (middle): (shoulder) adduction
• Picture 3 (right): (hip) flexion
7 One mark for each correct label.
• (top left): sagittal plane
• (top right): frontal plane
• (bottom right): transverse plane
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
8
• Transverse is side to side, e.g. somersault
• Longitudinal is top to bottom, e.g. pirouette
• Frontal is back to front, e.g. cartwheel
7
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
9
a Labels as follows:
• Third class lever
• Effort in the middle
• Order of labels: fulcrum, effort, load or load, effort, fulcrum (as long as effort is in
the middle)
• Effort arrow pointing up and load arrow pointing down
b Sagittal plane and transverse axis
10 Example answer provided in workbook.
The cardiovascular and respiratory systems
Practice questions (page 16)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1
• Arteries
• Capillaries
• Veins
2
• Systemic circulation = heart body heart
• Pulmonary circulation = heart lungs heart
3 One mark for each structure with a maximum of two marks for the structures of each
blood vessel.
• Arteries: thick walls, small lumen, elastic walls
• Capillaries: small lumen, one cell thick, large surface area
• Veins: thin walls, large lumen, have valves
8
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
4
5
6 Divides the heart into right and left sides
9
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
7 One mark for each correct definition.
Key term Definition
Heart rate The number of times the heart beats per minute (1)
Stroke volume The volume of blood pumped out of the heart per beat
(1)
Cardiac output The volume of blood pumped out of the heart per minute
(1)
8 One mark for each blank filled in correctly.
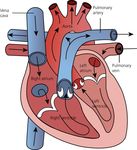
Deoxygenated blood returns back to the heart through the vena cava and enters the right
atrium. It is then pumped through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. From here
blood travels up through the semilunar valve into the pulmonary artery towards the lungs
where it is oxygenated. This oxygenated blood leaves the lungs and is transported through
the pulmonary vein into the left atrium. From here it is pumped through the bicuspid valve
into the left ventricle. The blood then passes through the other semilunar valve and out of
the heart via the aorta to the rest of the body.
9
• Systole is when the heart contracts
• Diastole is when the heart relaxes
10 One mark for each blank filled in correctly.
Air enters the body by being drawn in through the nose. It then passes over the vocal cords
of the larynx and into the trachea. This divides into two bronchi. The right bronchus goes
into the right lung and the left bronchus goes into the left lung. The bronchi then divide up
into smaller bronchioles which enable the air to pass into the alveoli where gaseous
exchange takes place.
10
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
11
a
1. Oxygen
2. Carbon dioxide
b
• Blood arriving in the alveoli has a higher carbon dioxide concentration than the
concentration of carbon dioxide in the alveoli so carbon dioxide diffuses from blood
to alveoli.
• Blood arriving in the alveoli has a lower oxygen concentration than the
concentration of oxygen in the alveoli so oxygen diffuses from alveoli to blood.
c
One mark for each correct key term.
Definition Key term
The volume of air that is inspired or Tidal volume
expired per breath
Frequency of breathing Breathing rate
The volume of air that is inspired or Minute ventilation
expired per minute
AO2: Application
12
• Transport oxygen to muscles
• Transport carbon dioxide to the lungs
13 Any three from:
• Blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart to collect the
oxygen the player needs for the game.
• Deoxygenated blood flows from the netball performer’s right ventricle to the lungs.
• The pulmonary artery transports the deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
• Oxygenated blood returns to the netball performer’s left atrium.
• Her pulmonary vein transports the oxygenated blood.
14 Cardiac output = stroke volume × heart rate
11
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
15
Activity Aerobic or anaerobic
Long jump Anaerobic
Tour de France Aerobic
100 m Anaerobic
Marathon Aerobic
16 Example answer provided in workbook.
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
17
• Muscle fatigue
• Muscle soreness / aches / pains
• Decrease in performance/performer slows down
18
• Aerobic exercise is continuous exercise usually over 3 minutes and anaerobic
exercise is short bursts of exercise up to 30 seconds.
• Aerobic exercise is low to moderate intensity and anaerobic is high intensity.
• Aerobic exercise uses oxygen and anaerobic exercise does not use oxygen.
• Aerobic exercise does not produce lactic acid, but anaerobic exercise does.
19
• Fartlek training
• To improve cardiovascular endurance the type of training needs to be long duration.
• Fartlek training is also similar to the demands of a football game as the speed and
intensity of the training are varied.
20 One mark for each of the following:
• A fixator muscle works with others to stabilise the origin of the agonist/prime mover
• In the bicep curl the trapezius contracts to stabilise the origin of the biceps.
• This enables the agonist to produce the desired movement.
Effects of exercise on body systems
Practice questions (page 22)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1 An increase in the number of capillaries
2 Any two from:
• Muscle fatigue
• Muscle soreness / aches / pains
• Decrease in performance/performer slows down
3 Vascular shunt
12
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
4
5 An elite performer’s recovery is quicker
6
• Long term
• Long term
• Short term
• Short term
AO2: Application
7 Any two from:
• Increase in heart rate/HR
• Increase in stroke volume/SV
• Increase in blood temperature
• Increase in oxygen delivery to the muscles
8
• Increase in tidal volume
• Increase in minute ventilation
9 Any four from:
• Increases blood flow to working muscles as they need more oxygen
• Directs blood away from non-essential organs which are not required during
exercise
• Increase in blood pressure due to an increase in the demand for oxygen by the
working muscles
• Increase in blood lactate/lactic acid because the muscles are working
• Increase in blood CO2 because muscles are working
• Increase in blood temperature helps control body temperature
13
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
• Vascular shunt/vasodilation of blood vessels to muscles/vasoconstriction of blood
vessels to other organs to control blood flow
10 Any four from:
• Decrease in resting heart rate
• Bradycardia
• Hypertrophy/bigger heart
• Stronger heart/stronger contraction
• Increase in stroke volume
• Increase in capillarisation around the heart
• Decreased risk of heart attack/angina/coronary heart disease.
11 Any two from:
• Increases bone density
• This makes the bones stronger
• Which can help to offset the effects of bone disease such as osteoporosis.
12 Example answer provided in workbook.
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
13 Any three from:
• Player A is fitter than player B because they have a lower resting heart rate or player
B is less fit than player A because they have a higher resting HR.
• When the graph flattens out the players are working at a sustained level.
• Player A works harder than player B through the game as their HR peaks highest.
• Player A performs a cool down as there is a gradual decrease in HR/player B does
not perform a cool down as there is a sudden decrease in HR
14 Answers need to give a benefit with an effect on performance and a rugby example.
• Hypertrophy of the muscle which can lead to an increase in
power/strength/speed, e.g. run faster to beat an opponent/tackle more
effectively.
• Increase in muscular endurance which means they can work harder for longer/at
a higher intensity/more resistance to fatigue, e.g. easier to perform effectively for
the duration of the game.
14
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
• Increase in flexibility/range of movement, e.g. less chance of injury/could stretch
further as they reach to tackle.
• Increase in tolerance to lactic acid/delayed anaerobic threshold which means
they can work harder for longer/at a higher intensity/more resistance to fatigue,
e.g. last the whole rugby game.
• Increased rate of removal of lactic acid which allows them to recover quicker, e.g.
increasing chances of lasting the whole game.
• Increased capillarisation at the muscles so more oxygen can reach the
muscles/aerobically fitter, e.g. work at a higher intensity or harder during the
game
Exam-style questions (page 25)
1
2
a
• Hip: flexion
• Knee: extension
15
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
b
• Muscle: quadriceps
• Plane: sagittal
• Axis: transverse
3
• (left) Frontal
• (middle) Transverse
• (right) Longitudinal
4 Accept either answer C or D
5
• Artery: transports blood away from the heart
• Vein: transports blood to the heart
• Capillaries: exchange points for oxygen and carbon dioxide/where diffusion of
oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place
6
• Aorta transports oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body/muscles.
• Vena cava transports the deoxygenated blood into the right atrium.
• Pulmonary artery transports the deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the
lungs.
• Pulmonary vein transports the oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
7 Second class lever
8 Any three from:
• Expiration is a passive process/caused by the relaxation of the respiratory muscles.
• The external intercostal muscles relax/the diaphragm relaxes.
• The volume of the lungs decreases and the pressure within the lungs becomes
greater than the pressure outside the body.
• Air is now forced out to equalise this pressure and expiration takes place.
16
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 1 Applied anatomy and physiology
9
• Aerobic exercise example to include low–medium intensity, e.g. long/middle
distance running, cycling, jogging
• Anaerobic exercise example to include high intensity exercise, e.g. sprinting
10 Their stroke volume increases
11
• Movement: muscle attachment enables movement
• Posture: gives correct shape as playing
12
• Connects muscle to bone
• Assists the muscle with pulling of the bone
• Makes bones move when a muscle contracts
• Gives stability/support
13
• Muscles work together as a pair/when one contracts the other relaxes.
• Example when the hamstring/quadriceps is the agonist the quadriceps/hamstring is
the antagonist or when the biceps/triceps is the agonist the triceps/biceps is the
antagonist.
17
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
Topic 2 Physical training
Components of fitness
Practice questions (page 28)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1
Fitness component Definition
Agility The ability to change direction quickly and under
control
Muscular endurance The ability of the muscle or group of muscles in the
body to repeatedly contract without rest
Speed The maximum rate at which a person can move over
a specific distance or the speed of specific body part
Flexibility Range of movement around a joint
2
• Balance is the ability to keep body mass or centre of mass over the base of support.
• Co-ordination is the ability to repeat a pattern or sequence of movements with
fluency and accuracy.
3
• For cardiovascular endurance: Cooper 12-minute run or multi-stage fitness test
• For speed: 30-metre sprint test
18
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
4
Fitness component Test
Reaction time Reaction time ruler test
Power Standing jump or vertical jump tests
Strength Grip strength dynamometer test or 1 Repetition
Maximum (1RM)
Co-ordination Wall throw test
5 One mark for each blank filled in correctly.
The length of the course is 10 metres and the width between the start and finish points is 5
metres. The four cones down the centre should be spaced 3.3 metres apart. The test starts
with the participant lying on their front with hands by their shoulders. On the word ‘go’, the
stopwatch is started and the athlete gets up and runs as quickly as possible around the
course to the finish without knocking over the cones. The time to complete the course is
compared to a national standardised table.
AO2: Application
6
7 D- a short pass in a game of football
19
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
8 Any two from:
• Cardiovascular endurance: fatigue is delayed/player is less tired
• So they can exercise whole muscle groups for the duration of the game/full 90
minutes
• Flexibility: less likelihood of injury/prevents stresses and strains to muscles and
joints
• Suitable example such as stretch/reach further in a tackle
9 One mark for each answer from: (only a maximum of one mark for each fitness
component):
• Power- needed to lift the weight/fast strong muscle contraction needed.
• Balance – needs a balanced position to successfully lift the weight/unbalanced in
danger of dropping the weight or failing to lift the weight above his/her head.
10 Example answer provided in workbook.
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
11
a Three students
b Two students
12
a Two players
b Any two from:
• Those who were excellent may have done a better warm-up/more stretching.
• Excellent performers may have longer arms.
• Mistakes could have been made when recording/accuracy of the test/validity.
• Those who were below average may have been recovering from injury.
• Those who were excellent may have had better co-ordination to jump and touch the
wall at the highest point of their jump.
20
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
13
a Flexibility
b
One mark for correctly stating that two scored excellent in the test
One mark for correct calculation and answer 2/14 = 14%
Applying the principles of training
Practice questions (page 34)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1
2
• HIIT
• Circuits
• Continuous
• Fartlek
• Weights
• Plyometrics
21
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
3
• Plyometric training: one from: strength or power
• Continuous training: one from: cardiovascular endurance or muscular endurance
4
• Pulse-raiser
• Mobility
• Stretching
• Dynamic movements
• Skill rehearsal
5 One mark each for the identification of each letter with a definition.
• F = frequency – how often you train /number of training sessions each week
• I = intensity –how hard you train
• T = time –how long you train for
• T = Type – the type of training to be considered that fulfils a specific need
6
• Low-intensity exercise
• Stretching
AO2: Application
7 Any two from:
• Gradually make each practice session more difficult/challenging
• Example of how this can be achieved through making drills harder, such as greater
passing distances/passing quicker
• Fitness example such as more running drills/higher intensity session/longer sessions
22
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
8 One mark for defining ‘overload’ and one mark for providing a suitable example.
Overload is where the body works harder than normal so that there is some stress and
discomfort.
Any suitable practical example which mentions increasing the frequency, intensity or time of
the training such as:
• Weight training - the lifter will eventually attempt heavier weights or an increase in
repetitions.
• Sprinter may add more high intensity work intervals.
• Games player may do more running to increase endurance, thus overloading the
body.
9 C- continuous
10
• The mistake is in going from press-ups to dips.
• Press-ups and dips are both arm/triceps exercises and parts of the body/muscle
groups need to be alternated.
11 Any two from:
• Bounding
• Hopping
• Jumping
12 Any three from:
• Duration of the work interval
• Speed/intensity of the work interval
• Number of repetitions/sets
• Duration of the rest interval
13 Must specify arm/shoulder exercises for a golf swing.
• Arm/shoulder circles
• Arm swings
14 Example answer provided in workbook.
23
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
15 Any three from:
• Fartlek training improves cardiovascular endurance which is needed in a game of
football that lasts a long period of time/90 minutes.
• It consists of both high- and low-intensity activity which is similar to a match where
the player will do low-intensity work/walk/jog and high-intensity work/run/sprint.
• Trains both the aerobic and anaerobic systems which are both needed in a game of
football where the pace of the game continually changes.
• Improves anaerobic fitness through the use of high intensity/sprinting activities.
16 Any four from:
• Warms up the muscles to reduce injury/reduce muscle soreness/stretch more
• Increases heart rate so more oxygenated blood can be transported to the muscles
• Increases the flexibility of muscles/joint/and the pliability of ligaments and tendons
which makes them more elastic and means the player can stretch more/reduces
injury
• Increases blood flow to the muscles so they receive more oxygen
• Increases the speed of muscle contraction which will improve reaction time
17
• Increasing the frequency of training so he is training more often
• Increasing the intensity of training so it becomes harder and places more stress on
the body
• Increasing the duration of training so he trains for longer
24
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
Preventing injury in physical activity and training
Practice questions (page 39)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1
Sport Personal protective equipment
Football Goalkeeper gloves/shin/ankle pads
Rugby Scrum cap/shoulder pads
Cricket Wicket keeper gloves/helmet/leg
pads/cricket box
2 Bend the knees and not the back
3 Example answer provided in workbook.
4 Any two from:
• Hazardous litter such as dog excrement/glass
• Posts
• Fencing
• Pitch surface e.g. if it is frozen in winter
• Other participants
5i
• Water/depth of water
• Chemicals/balance of chemicals in the water
• Access to pool/surface of surrounding area
• Equipment used in swimming session
• Presence of others/lack of awareness of others
• Teacher-pupil ratios
• Presence of trained lifeguard/first aiders
25
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
ii Any three from:
• Use of specialist equipment to help with safe access into/around the pool
• Ensure trained lifeguards/Afirst aid staff are present
• Provide 1:1 instruction/ low teacher-pupil ratio
• Do a facility risk assessment to identify how disabled individuals could potentially be
harmed in a swimming pool environment
• Ensure knowledge of individual needs/potential health issues
6 Any three from:
• Any litter that someone could slip on/equipment that has been left out
• Damaged equipment
• Inappropriate footwear
• Number of participants/too many
• How close the wall is from the edge of the court
• Open doors or windows/blocked fire exit
• Quality of the lighting
AO2: Application
7 Stops slipping/creates more friction
8 Provides stability/support for the foot/ankle
9 To protect the brain which is a vital organ
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
10 Any four from:
• Age of the performers, e.g. playing in their appropriate age group
• Sex: girls should not be playing against boys in some age groups
• Skill level: the higher the skill level/techniques the less likelihood of injury/skills
and/or techniques need to be taught correctly
• Level of ability: need to play in a league appropriate to ability level – a participant
may try too hard if the standard is too high
26
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
• Fitness levels: appropriate to the level being played, for example having the required
stamina/flexibility/strength to participate safely
11
a Any three from:
• Check the equipment to see whether it is broken or in a safe position, i.e. not too
close to other equipment.
• Make sure the flooring is dry/clean so no one slips.
• Make sure that any open windows/doors are not protruding which could result in
someone walking into them.
• Check free weights, e.g. any loose collars so weights are not going to drop off a bar.
• Make sure that all participants are behaving sensibly and safely, e.g. not trying to lift
too much/using correct technique. Area is not too crowded.
b Any three from:
• Teach correct use of equipment/correct technique
• Demonstrate how to use equipment safely
• Include a warm-up/cool-down
• Make sure everyone is following the rules/protocols
• Needs to make sure that training is suitable for the participants, depending on
age/health/fitness/any injury or medical conditions
Exam-style questions (page 42)
1
• Cardiovascular endurance: the ability to exercise continuously without tiring.
• Power: a combination of strength and speed.
2 Any two from (maximum one mark from each component):
• Balance can help fluency in movement.
Suitable example: in a floor routine a gymnast has to hold a position/named balance
such as arabesque/handstand/headstand/performing on the beam.
• Co-ordination: A gymnast is required to perform a sequence of movements with
fluency and accuracy.
27
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
Suitable example: floor routine where there is a succession of different
techniques/handstands, somersaults and twisting somersaults/vaulting – has to run, jump
and twist.
3 C- Muscular endurance
4 Sit and reach test
5 One mark for the definition and one for a suitable example.
• Specificity is when training is relevant to the activity or the type of sport
• Examples include:
A power athlete would use weight training/HIIT.
An endurance performer would use continuous/fartlek training.
6
Name Age Score Rating
Alan 54 34 Good
Adam 22 20 Fair
Chris 34 29 Average
Elijah 30 34 Average
Tim 43 39 Good
7
• (FITT = frequency, intensity, time and type)
• Frequency – they will train more often/have more training sessions
• Intensity – they will train harder, for example lift heavier weights/do more
reps/sets/run sprints faster or equivalent
• Time – they will train for longer, for example a one-hour session could be increased
to 90 minutes or equivalent
• Type – they would need to decide on the type of training that fulfils their needs, for
example continuous/fartlek/interval training that can improve their
28
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
cardiovascular/muscular endurance as the game lasts 90 minutes or weight
training/plyometrics to improve their power so they can run faster, jump higher
8
• Pulse raising: any one from – jogging/gentle running/skipping/cycling
• Dynamic movements: any example that involves a change of speed and direction,
e.g. shuttle runs
9 Any three from:
• Allows the blood to circulate to transport oxygen to the muscles, tendons and
ligaments for repair
• Aids recovery by stretching muscles
• Increases the removal of lactic acid which reduces the risk of muscle soreness and
stiffness
• Prevents blood pooling in the veins, which can cause dizziness
• Allows the body to gradually return back to normal which can avoid light-
headedness or feeling faint
10 Any one from:
• Head guard
• Mouth guard
• Shoes
• Groin guard/chest guard (for men/women respectively)
• Hand wraps
11
• Ensure they wear personal protective equipment with example: such as scrum
caps/shoulder pads to try to avoid injury
• Wear the correct footwear with example e.g. on soft ground wear studs to stop
slipping
• Participate in the appropriate level of competition with any of the following
examples: e.g. not playing at too high a level as players could try too hard and risk
injury/playing in the correct age group as playing against older participants who will
29
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
be bigger and stronger could lead to injury/fitness level needs to be good enough to
avoid injury/be taught the correct technique e.g. tackling to avoid injury
• Warm-up before the match to stretch the muscles to try to reduce the chance of
injury
12 Any three from:
• Speed is a major fitness component for the triple jump.
• The triple jumper needs speed to create momentum/achieve a long jump/win
• The run up is short so the jumper needs to gain as much speed as they can as quickly
as possible
• Most speed is required at take-off
13 Any three from:
• Chemicals in the water
• Wet/slippery surface of surrounding area
• Equipment around the edge of the pool
• Other swimmers
• The depth of the water itself; this could bring the risk of drowning
14 Any three from:
• A batsman may have to respond quickly to a fast bowl to try to hit it.
• With a spin bowler, the ball can spin off the pitch so the batsman needs to be able to
respond to this.
• Wicket keeper/close defender may have to respond quickly to try to catch the ball or
stop it.
• Batsman will have to respond quickly to a decision to run a quick single.
15 Any four from:
• Plyometric training develops power.
• A basketball player needs power to be successful in a game.
• Therefore, plyometric training is relevant to a game of basketball/specificity.
• Power is needed in the legs for rebounding, jumping to intercept/a jump ball.
30
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 2 Physical training
• Power is need in the arms for a hard/fast throw.
16 Any six from:
Arguments for (maximum 3 marks):
• Continuous training is long duration training without any rest periods.
• A game of tennis is long duration, so it is a relevant method of training.
• It improves cardiovascular endurance/stamina/aerobic system which is needed in a
tennis match.
• Activities in continuous training often involve running and this is specific to tennis
where a lot of running in performed.
• It’s a very easy/simple method of training/with no equipment needed.
Arguments against (maximum 3 marks):
• However, it should not be the only method of training that a tennis player includes
in their training programme.
• Other methods such as weight training are important to develop power.
• HIIT training develops speed/anaerobic endurance.
• Plyometric training is suitable for developing arm and leg power.
• Fartlek training could be a more suitable method because it varies the intensity of
activities, which is similar to a game of tennis.
• Interval training can improve both aerobic and anaerobic fitness.
• Circuit training could be used with skill stations so skills can be improved.
31
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
Paper 2: Socio-cultural
issues and sports
psychology
Topic 3 Socio-cultural
influences
Engagement patterns of different social groups in physical activities and sports
Practice questions (page 46)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1 A- Sport England
2 a True / b False
3 Active Lives Survey
4 One mark for correct overall order: b, c, a
5 One mark for each blank filled in correctly.
Sport England is an organisation which tries to help people in communities develop a
‘sporting habit for life’ via a variety of different schemes and initiatives. National Governing
Bodies (NGBs) are organisations that assume specific responsibility for their sport (for
example, British Cycling). An annual report which measures and then provides an update on
the sport and activity patterns of various sections of society in England is called Active Lives.
The social groups measured are based on ethnicity, disability and gender. The government
department with responsibility for government policy related to sport is called the
Department for Media Culture and Sport (DCMS).
32
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
6 Any four from:
• Facility access problems
• Lack of adapted/specialist equipment
• Lack of confidence/low self-esteem
• Lack of suitable activities to participate in
• Low income; can’t afford the costs associated with participation
• Lack of specialist coaching
7 Any four from:
• poor health
• low levels of confidence/low self-esteem
• perceived) lack of fitness
• lack of appealing/suitable activities
• accessibility issues (into/around facilities)
• transport issues
8 Any four from:
• to manage their stress levels
• to provide a feel-good factor
• to increase their sense of well-being
• to maintain/increase their health and fitness levels
• to increase life expectancy
• to provide a source of fun/enjoyment
• to give a sense of belonging
• to increase skill levels/provide a new interest
33
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
9 Any four from:
• provide you with a positive role model to aspire to if they play sport too
• provide encouragement to play sport
• give lifts/arrange transport (to training/competitions etc)
• provide funding/money to support involvement (eg pay for kit/equipment/coaching
etc)
• provide emotional support/support during competitions
10 One mark for each correct definition given in the table below.
Key factors Key factors defined
Promotion Convincing people they should participate
Provision Ensuring people have the facilities, equipment and
coaching necessary to engage in physical activity
Access Giving people the opportunity to participate by making it
easier to engage in sport (e.g. via wheelchair
ramps/adapted transport)
34
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
AO2: Application
11 One mark for each correct response.
Possible strategy Examples
Provide more information and education Use of promotional schemes and adverts
on the benefits of regular sports such as This Girl Can; Change4Life; Local
participation authority initiatives
Increase the availability of facilities for Local sport/leisure centres/health and
people to use to keep them active fitness clubs/sports clubs stay open for
longer
Increase accessibility of facilities Improved transport arrangements to
facilities, e.g. free/subsidised bus/minibus
travel; wheelchair ramps; disabled changing
facilities
Decrease costs of facilities Concessions for adults, e.g. at local leisure
centres; cut price admission/membership
fees to clubs/gyms
Introduction of adapted activities for older Adapted games such as walking
people and those with disabilities football/basketball/netball; touch rugby
Improved childcare provision Creche/nursery provision/playgroups so
parents can exercise/play sport
12 Any three from:
• Parents/other family members (e.g. sisters/brothers) are actively involved in sport
themselves and act as positive role models (e.g. keep fit/playing netball; swimming)
• Parental support is available (e.g. via finance to pay for equipment, e.g.
golf/skiing/coaching/membership fees)
• Parents explain/promote the benefits of sport (e.g. health and fitness; social and
mental)
• Parents encourage positive morals/sporting etiquette (e.g. sportsmanship/fair play:
shaking hands at the end of a sporting contest)
35
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
13 One mark for each correct example given; maximum two marks per box.
Environment/Location Activity examples
Fistral Beach, Newquay • water sports, e.g. surfing
• beach volleyball
• swimming
Three Peaks, Yorkshire • mountain walking
• rock climbing
• hill running
Aviemore, Scotland • mountain walking
• rock climbing
• skiing
• mountain biking
• mountain walking
14 Any three from:
• Via observation/watching high-level elite performers in the media such as Premier
League footballers on Sky TV
• Via looking up to/admiring individuals at your school/local club
• Via PE teachers setting a positive example to follow at school
• Via sports coaches who visit your school/club to coach specific activities
• Parents/family members/peers can act as positive role models via active
participation themselves
15 Swimming increased. Any four for 2 marks from:
• Relatively cheap (e.g. in the sea)
• Good availability of facilities/local pools
• Easy to do alone/fit in alongside other work/family commitments
• Viewed as a good non-weight bearing activity to maintain health and fitness as a
lifelong sporting activity
• Positive role models to aspire to (e.g. Adam Peaty)
36
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
Racket sports (e.g. tennis) decreased. Any four for 2 marks from:
• Quite expensive (e.g. court hire/club membership fees)
• Lack of (tennis) courts to access (e.g. indoors)
• Negative impact of climate/poor weather
• Lack of provision in school PE programme
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
16 Any four from:
• Inactivity levels generally increase with age.
• The sharpest increase is at 75 (i.e. 22% to 49%).
• Sport is often perceived as being for younger people rather than older people.
• Some of older people lack confidence/feel very self-conscious about exercising, etc.
• Participation may be negatively affected by illness/poor health/medical conditions.
17 Any four from:
• Most activities have shown an annual increase in participation,
• particularly in adventure sports (e.g. hill walking, climbing, etc.) which have risen by
600,000
• and walking for leisure (which has risen by 500,000).
• Fitness activities have also seen a big increase in participation of 400,000.
• Team sports participation has remained constant.
• Racket sports are the only activity which have seen a decrease (down by 100,000).
37
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
18
• Using/becoming involved in promotional campaigns (e.g. This Girl Can)
• Ensuring equal access to sports facilities, e.g. via equal opportunities
policies/challenging discrimination, e.g. in golf clubs
• Providing taster sessions/women-only sessions in their sport
• Using female role models to inspire participation (e.g. Jessica Ennis-Hill; This Girl Can
adverts)
• Training more female sports coaches in their sport to address possible
religious/cultural restrictions
Commercialisation of physical activity and sport
Practice questions (page 52)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1 a True
b
Amateur rugby Sport
New kit via a legal company Sponsorship/commerce
Publicity photo in a local Media
paper
2 Any two from:
• Twitter
• Facebook
• Snapchat
• Instagram
• YouTube
• Strava
3 D- Badminton
38
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
4 One mark for each blank filled in correctly.
There are a variety of different types of media which give a high priority to covering
sport including social media, the internet, television and newspapers.
TV companies spend huge sums of money on the broadcasting rights to sporting
competitions and events, including England’s Test Match cricket and Premiership
football matches via Sky Sports. If you want to watch certain sports, even on
subscription channels, you have to pay an extra fee to do so. This is called pay per
view and it has proved to be very popular in coverage of the sport of boxing (for
example, Fury versus Wilder). YouTube has become an important outlet for sports
media companies, including Sky Sports, which uses it to provide highlights from
Premier League football matches. Sports coverage is also directly available for people
to watch via social media companies, such as Twitter. While the media tends to focus
on covering mainstream sports such as association football, rugby, golf and cricket, BT
Sport has provided a platform for coverage of the Women’s Super League (WSL),
which has given women’s football much needed income and exposure, promoting
female participation.
5 One mark for each correct definition in the table below.
Term Definition
Commercialisation The influence of commerce/business on an industry
(e.g. sport) to make a profit.
Golden Triangle Sport, the media and sponsorship are closely linked
and have a positive mutually beneficial relationship.
Sponsorship The financial support/money given to a
sport/sports event/sports performer/organisation
by an outside agency/person/organisation for the
mutual benefit of both parties.
Media The means of mass communication (e.g.
broadcasting, publishing and the internet)
39
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
6
AO2: Application
7 True
8 One mark for each correct answer.
Football club Sponsor’s name of their ground
Stoke City Bet 365 Stadium
Wigan Athletic DW Stadium
Leicester City King Power Stadium
Burton Albion Pirelli Stadium
Manchester City The Etihad
AFC Bournemouth Vitality Stadium
40
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
9 One mark for each correct answer.
Type of media Example of how it promotes sport
TV/visual Live matches/sports events via TV channels such as
ITV/BBC/Sky Sports/BT Sport
Internet Websites of major teams; high profile athletes
publishing facts and figures about themselves to
keep fans up to date on what is happening
Social media People create/share/discuss sports-related
content;
Teams/athletes have their own accounts on
Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Snapchat, YouTube
Newspapers/magazines Print fixtures/results/match reports/interviews
with sports people (e.g. Daily Mail, FourFourTwo,
etc.)
10 Any four from:
• Over-reliance on sponsorship; withdrawal of sponsorship from an
individual/team/event
• Focus on a narrow range of sports; minority sports miss out
• Minority groups such as women/disabled people get less sponsorship
• Commerce/sponsor may reflect badly on a sport (e.g. a betting/alcohol company)
• It can lead to deviant behaviour; increased pressure to win to maintain rewards
• Possible over-influence of sponsors on how sport is played (e.g.
rules/timings/scheduling of matches/events)
41
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
11 Any six from:
Advantages of commercialism (maximum of 3 marks):
• Allows athlete to earn income as a full-time job so they can train to improve
performance/pay the fees of specialist coaches; can pay for medical
support/treatment etc.
• Gain maximum exposure/increase status to promote their personal brand; become
known as a better athlete
• Can lead to additional roles post-playing career within the sport (e.g. as a TV pundit)
• Relieves financial worries e.g. can fund education, scholarships to University
• Provides free clothing/equipment (sponsors supply kit etc.)
Disadvantages of commercialism (maximum of 3 marks)
• Can result in deviant behaviour due to pressure to succeed/win at all costs
• Generally, favours male over female and able-bodied over disabled people
• Sponsorship might be short-term
• Performers may have to advertise a product they do not like/is a disadvantage to
them to wear (e.g. unable to wear Nike Vapor Fly shoes as a distance runner)
• The intrusive demands of sponsors for public appearances/filming of adverts
12 Any six from:
Advantages to sponsors (maximum of 3 correct points)
• Increased publicity/opportunity for sponsor to advertise/promote a product/service
to a widespread audience (e.g. on TV)
• Raise awareness/advertise brand name/develop a positive healthy image
• Companies get tax concessions; opportunity of providing hospitality for
clients/business partners
• Improve company morale via free tickets to sports events
• Increased sales/demand for products/increased profit
• Increased status of product(s) by being linked to successful sports performers/high
profile events
42
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
• Disadvantages to sponsors (maximum of 3 correct points)
• Reflects badly on a sponsor, such as negative press via poor athlete behaviour (e.g.
Ben Stokes and New Balance)
• Unethical companies are ‘unsuitable’ sponsors in sport (e.g. alcohol, gambling, fast
food companies)
• Large investment can backfire if success is not achieved (e.g. if an individual or team
fails to qualify for a major competition) or an event/competition does not take place
(e.g. due to coronavirus)
13 Any four from:
• A sport (e.g. association football) is presented to business (e.g. Barclays/Emirates
etc...) as a means of advertising its product(s)
• The business sponsors the sport (e.g. Barclays Premier League; Emirates FA Cup
(etc...) to advertise/promote its product(s)
• The sport (e.g. association football) is shown via the media (e.g. TV) which promotes
its product(s)
• Fans/viewers of the sport see the advertising
• and buy the business product(s) (e.g. financial services; airline tickets)
Ethical and socio-cultural issues in physical activity and sport
Practice questions (page 57)
AO1: Knowledge and understanding
1 a True
b False
2 Any four from:
• Increase in performance
• Excites/arouses the brain; increased adrenaline/heart rate; increased
confidence
• Increased alertness/focus/concentration; decreased reaction time/increased
speed of reactions
• Delayed fatigue/increased ability to train/continue for longer; decreases pain
43
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
3 One mark for each blank correctly filled in.
Anabolic steroids are banned drugs which have been widely used to cheat in sport
for a number of years. They are an artificial (chemically synthesised) form of the
male hormone testosterone. They help the athlete to make rapid increases in
strength by promoting bone growth and developing muscle mass. They also aid
recovery and repair of muscle fibres after high-intensity movements such as
sprinting, which allows athletes to train harder and more frequently. Steroids are
often used as a ‘training drug’ in sports such as weightlifting, sprinting and other
power-based events.
Stimulants are banned substances such as caffeine and amphetamines which can be
used to increase alertness and competitiveness. They aid performance in games by
reducing reaction time, speeding up reflexes and decreasing feelings of fatigue.
Stimulants are commonly used in team contact sports, such as American football,
and sports which require quick reaction times, such as baseball.
Beta blockers are banned performance-enhancing drugs which help a sports
performer to keep calm by blocking the effect of the hormone adrenaline. This has
the effect of reducing a performer’s heart rate, blood pressure and any anxiety they
may be feeling, which helps prevent their hands shaking. This is sometimes exploited
in target-based sports such as shooting and archery.
4 One mark for each correct answer.
Reason for taking PEDs Explanation
Win ethic Pressure to succeed leads to a win-at-all-costs mentality
National pride Pressure to succeed for the nation from the media and public
Extrinsic rewards Pressure to succeed to receive financial gain (eg sponsorship)
Physical benefits Pressure to improve physical condition by decreasing
recovery time from training and injury
Psychological benefits To boost confidence and to increase aggression
Levels the playing field The belief that other competitors are taking drugs, so
without them they will not be able to compete equally
44
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
5 Any three from:
• Long ban/harsh punishment
• Loss of trust/reputation/respect from fans/family/peers
• Loss of credibility
• Loss of income/sponsorship deals/medals/titles
• Negative role model; sets a bad example to other athletes/the young
• Arouses the suspicion of other athletes
• Negative impact on performer’s health (e.g. heart disease/strokes)
6 One mark for each key term.
Definition Key term
Sporting behaviour that shows fair play Sportsmanship
and respect for opponents, as well as
gracious behaviour when winning or
losing
Human behaviour which goes against Deviance
the norms and values of society,
including going against the rules of sport
Sporting behaviour to gain an Gamesmanship
advantage by stretching the rules to
their absolute limit, but not actually
cheating!
AO2: Application
7 a Deviance
b Sportsmanship
c Gamesmanship
d Deviance
e Sportsmanship
45
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
f Deviance
g Sportsmanship
h Gamesmanship
I Deviance
J Gamesmanship
8 Example answer provided in workbook.
9
• Example PED: Beta blockers
• Reason: Slow down the heart rate and have a calming and relaxing effect
that is beneficial in sports requiring a steady hand/fine motor control such
as golf.
10 One mark for example and one for each negative consequence (up to 3 marks):
• Example from: cycling/athletics/weightlifting etc.
• Damage a sport’s reputation; a sport becoming known for cheating
threatens its integrity
• Sport loses its credibility, due to strong association with drugs and cheats
• Lack of trust in performances by fans; drug use ‘clouds the successes of
clean athletes’
• Loss of sponsors/income/lottery funding
• Provides negative role models to young children/aspiring athletes; they will
believe that they cannot compete if they don’t also take drugs
46
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
11 One mark for each relevant explanation/answer.
Reason for player violence Explanation/example of this
Win ethic Result is all-important because of team or individual
position in the league/rewards at stake
Nature of the game High contact sports are more likely to lead to violence
(e.g. in ice hockey and rugby)
Negative reaction to provocation Crowd abuse/chants; ‘sledging’/violent physical contact
from opponents
Frustration/disappointment Team losing; playing badly; poor decision by an official
Dehumanised view of opposition Protective helmets and clothing which turns opponents
into ‘objects’ rather than people to be respected
Emotional intensity ‘Cauldron effect’ of a venue; over intense psyching up of
players by the coach
AO3: Analysis and evaluation
12
• To ensure respect amongst players and to the officials
• To decrease the risk of injury to individuals taking part
• To help create a pleasant and enjoyable atmosphere to play in
• To provide positive role models and improve the reputation of the sport,
which might encourage more to play/watch the sport
• To help ensure sport can be played without negative deviant aspects being
evident such as aggression/foul play/gamesmanship etc.
13 Any four from:
• Trends illustrate a large decrease in red cards over the decade/10 years of
staging of the World Cup tournaments
• Indication of improved player behaviour/less deviance
47
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
• Due to introduction of VAR/technology keeping a close eye on player
behaviour/assisting with refereeing decisions and decreasing frustration in
players
• Players more aware of responsibilities and need for improved behaviour
• Increased need to maintain discipline to protect the image sponsors demand
• Increased need to display sportsmanship/fair play on the field of play as
positive role models
Exam-style questions (page 62)
1 False
2 True
3 Any two from:
• It will improve communication skills.
• Increase the ability to make friends with people of shared interests/become more
approachable.
• As part of a weight loss plan for an overweight individual it can increase confidence
to interact with others.
4 Any three from:
• Sport often thought of as being for young people/not for older people
• Lack of confidence/low self-esteem
• Negative impact of medical conditions/illness
5 Any three from:
• Lack of time/traditional childcare responsibilities
• Lack of confidence/negative body image
• Safety concerns/fear
• Funding issues/costs of participation
• Male domination
• Lack of female role models
• Sexism/discrimination
48
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021TOPIC 3 Socio-cultural influences
6 Treating people differently/acting on a prejudice/excluding from participation, especially
on the grounds of race, age, or sex.
7 Any three from:
• Racism/discrimination
• Actively discouraged by parents/peers
• Low status given to sport/preference for academic work
• Conflict with religious observances/dress codes
• Fewer ethnic role models/less media coverage
• Stereotyping/channelling still exists
• Fear of rejection/lower self-esteem
8 Gaining an advantage/trying to win by stretching the rules to their absolute limit (not quite
cheating)
9 C- Snooker player
10 Any three from:
• Health problems/overweight/obesity/illness
• Disability
• Lack of facilities/equipment/coaching expertise
• Lack of interest/motivation
• Lack of role models/encouragement to participate from family/friends
• Discrimination/sexism/racism/ageism
• Cultural/religious restrictions
• Lack of confidence/low self-esteem/poor climate/location
• Costs/too expensive
• Work/family responsibilities/lack of time
49
OCR GCSE (9–1) PE Workbook© Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2021You can also read