5G and the future of the Internet - by Angel Gurria, Secretary-General, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) - ECI Telecom
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Europe I 2020 The Magazine that Provides Thought Leadership for ICT Decision Makers www.connect-world.com 5G and the future of the Internet by Angel Gurria, Secretary-General, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
Net Neutrality
How transport providers can
profit from Net Neutrality by
embracing 5G
by Hayim Porat, CTO, ECI
The article outlines how 5G can turn this situation on its
head. It shows how 5G enables evolution to a situation
where preferred access with service assurance is avail-
able to all fixed and mobile users, and on a dynamic,
per-use basis. Consumers will be able to enjoy
high-definition video, obtain lightning responses for
gaming, or experience real-time virtual reality, from
wherever they happen to be.
Hayim Porat joined ECI, as CTO, to lead its innovation center and spearhead the efforts in the areas of NFV and SDN in
2015. Hayim is a key contributor to the company’s ELASTIC networks strategy which bridges SDN/NFV, big data,
security and cloud services with advanced networking. Hayim brings vast experience in similar positions in the telecom-
munications hi-tech industry, which include work at Toga Networks, Tejas and Ethos. Hayim holds a B.Sc. in computer
science from the Technion and a MBA from Tel Aviv University.
Net Neutrality – Debate and
opportunity
U nder a net neutrality regime, Internet
Service Providers (ISPs) must treat all
public Internet traffic equally. They may
not intentionally block, slow down, or
charge users money for specific online
content.
Leading proponents of net neutrality, such
as human rights advocates and smaller
content providers, say it is needed to
protect freedom of information exchange,
create a level playing field for competition, the ISPs themselves and larger content Internet, and from their perspective, reduc-
and promote service innovation. providers. They claim that mandating es competition. They also state that neutral-
equal treatment of Internet traffic reduces ity raises operating costs, or removes a
The main opponents of net neutrality are financial incentives to build out the public mechanism to compensate for these costs,
which they must then pass
along to end-users.
While net neutrality
enforcement varies greatly
around the world, looking at
the big picture, we can
conclude that net neutrality
will largely exist. The good
news is that regulation
always creates new oppor-
tunities. In this WP, we
focus on how transport
providers in particular can
profit from assisting new
5G services to “work
around” net neutrality
barriers.
Europe I | 2020 . 30Net Neutrality
Working around a neutral (e.g. AWS, Azure),
Internet today or by large
content-neutral
Contrary to popular belief, net neutrality cloud providers
regulations do not affect everyone involved (e.g. Equinix).
in the delivery of Internet services; they Enterprises often
only apply to ISPs supporting the public connect directly to
Internet. They do not apply to content a private internet
providers, nor to telcos who use their via dark fiber or
transport networks to deliver access to WDM. Other users
ISPs. Even when the telco and ISP are the obtain various tiers of dedicated or guaranteeing an ability to obtain 5G’s
same corporate entity, regulators treat these preferred shared access from the telco to advanced service capabilities end-to-end.
functions differently. the private internets in the same way they 5G is much more than a next generation
access the public Internet. wireless technology. 5G is revolutionary in
Here are three ways that end-users and that it is hard-wired for multiservice
content providers legally overcome a Content caching capabilities. Based on the 3GPP standard, a
neutral Internet today, which treats all 5G SIM card can support multiple service
traffic equally, to obtain or deliver higher Content caching enables content and profiles with specific network access
performance. application providers to offer highly methods associated with each profile. An
responsive services to end-users. In effect, end-user can program-in different levels of
Preferred access the content/application providers move performance for different services. For
their presence closer to the end-user. While example, an end-user might specify a 5G
For regulatory purposes, the public Internet ISPs enable caching services, this does not eMBB broadband for regular web brows-
comprises ISP routers that implement break net neutrality. ing, but select a mixed profile of URLCC
“neutral” routing decisions based on the with eMBB broadband when accessing
Internet Protocol. Transport facilities that Dynamic transport opportu- high-definition streaming or AR/VR
connect traffic from end-users to these nity for a 5G world services. This multiservice media capabili-
routers are not part of the regulated public ty is a telecom first, with enormous poten-
Internet. Large businesses take advantage A proposition for change tial for disruptive service models. It can get
of this by paying telcos for dedicated even more interesting with the introduction
connections to ISPs. This removes To summarize the situation until now, of eSIMs that can fuel an even more
bandwidth limitations caused by shared end-users and content providers will find a competitive environment.
access with other users. Moreover, when way to ‘work around’ regulated ISPs to
businesses pay more for access deeper into achieve better performance, when they can This will give the ability for 5G users to
an ISP’s Internet infrastructure, they also afford it. In the case of end-users, this is pay for and obtain premium connectivity to
remove time-consuming router hops, primarily large businesses paying telcos for the public Internet or to private internets, to
further improving their performance preferred access – using fixed landline obtain the highest level of end-to-end
experience. facilities, and on a dedicated basis – to the performance. This is conceptually similar
public Internet or to private internets. to what businesses pay for today, with one
Consumers, who cannot afford dedicated major difference. Because 5G is mobile,
connections, can pay for higher shared The proposition is that 5G will turn this on and users only access Internet applications
bandwidth at the telco broadband network its head. It will enable an evolution to intermittently, this preferred connectivity
gateway (BNG). This provides their traffic where preferred access with service would not be permanent. It would be setup
with some preference by the telco transport assurance is available to all fixed and dynamically on a per-use basis.
network on its way to and from their select- mobile users, and on a dynamic per-use
ed ISP. basis. Telcos will provide this dynamic 5G has the ingredients to
preferred access, either through enhanced make this succeed
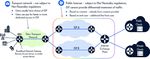
Private Internets connectivity to the public Internet, or via
connectivity to private internets. The major hurdle for enabling mass-market
With private internets, end-users and premium connectivity, delivered dynami-
content providers bypass the public This process will start with 5G users, to cally, is the upfront cost. In the case of
Internet to obtain faster speeds and lower meet their unique needs. Once the mecha- fixed networks, where this would entail
latencies. Typically, private internets are nisms are in place, telco transport providers upgrading the entire DSL/GPON/DOCSIS
provided by large content providers as an will be able to extend this capability to all infrastructure all the way to transport and
extension of their cloud hosting services fixed and mobile users. OSS/BSS systems, in the hope that enough
Evolution of Preferred Connectivity to the Internet users will pay a premium, makes no
economic sense.
Today Future 5G is a candi-
Type of user Businesses Consumers and businesses date for driving However, 5G’s mobile and multiservice
Access media Fixed (landline) Mobile and fixed
this change nature brings multiple economic and
Duration Permanent – full time Dynamic – per use technical advantages that makes implemen-
Opportunities often tation much more feasible. It has all the
Service Yes, taking advantage of
Yes, by leveraging dynamic arise in response to a ingredients in place to assign connectivity
orchestration and restoration
assurance dedicated facilities
mechanisms when needed problem. In the case of resources dynamically – from a pool of
5G, the problem is shared resources – to specific service
Europe I | 2020 . 31Net Neutrality requests: cloud-based management and control, the moving parts. 1. A technical basis already exists including multi-access edge computing Combine these dynamic transport capabili- for dynamic allocation of resources for (MEC), and a virtual and disaggregated ties with all of the favorable mobile/5G mobile services. Mobile networks are built next generation core (NGCORE). This aspects listed above – foundation for with media management and multiple obviously leads to implementation using dynamic allocation of resources, largest service types in mind, with the inclusion of resource pooling. Internet user group, tiered pricing IMS (IP multimedia subsystem) since 3rd established, intermittent use of services generation mobile networks. This created a Solution lies with a dynamic telco transport and connectivity, architecture based on technical foundation for allocating resourc- network shared resources in RAN and core –the es to services on the fly. MNOs have also However, there are obstacles to delivering conclusion is that telcos have a solid learned from IMS how they can profit from all of 5G’s service capabilities end-to-end. technical and economic basis to build the value-added end-user services (e.g. text While we can create tunnels with specific desired solution. messaging, conferencing) or infrastructure performance characteristics through the Telcos can leverage their dynamic services (e.g. authentication, accounting) RAN (radio access network and front haul) transport infrastructure to engineer a beyond pure connectivity. for the different services, there may be solution based on statistical sharing of 2. Mobile, as the primary media for bottlenecks in the end-to-end connectivity resources in this infrastructure, to deliver Internet use, will create demand for to the content or application provider. preferred connectivity dynamically, and on preferred connectivity services. Mobile is These would inhibit the 5G user from a per-service use. Another way to look at already the main media for Internet content getting the desired or expected perfor- this is that telcos become an intermediary, and applications consumption, and its mance. connecting the shared resource architec- share versus fixed media is increasing. Any performance bottlenecks preventing tures in the 5G RAN and Core, with their According to the Visual Networking Index, 5G users from obtaining an optimal own shared resource solution. As 5G by 2022, mobile and Wi-Fi only devices Internet experience lie either in the telco mobile users become the largest group of will account for over 75% of Internet transport network connecting the RAN to Internet users, this suddenly makes traffic. the public Internet, or within the public time-sharing of these transport resources 3. Mobile broadband packages are Internet itself. However, net neutrality economically feasible. This could never metered, laying the groundwork for 5G prohibits doing anything within the public have been the case for fixed services or users to pay for tiered connectivity Internet that is service-specific. Conse- single mobile service mass market. services. Compare this with fixed broad- quently, it’s up to the telco transport The end-user benefits from a guaranteed band packages that are not metered. network to provide the solution to the 5G high-speed experience for an incremental Mobile network operators (MNOs) have performance bottleneck problem, or as fee. It is also feasible that the content or educated end-users to pay premiums for good a solution as possible. application provider can subsidize the tiered levels of mobile connectivity. They In other words, the transport network must preferred access cost. created mobile plans based around a implement “premium connectivity services This is indeed a golden opportunity for neutral Internet, including arrangements for a price – delivered on a per-use basis” telco transport providers serving mobile that take advantage of net neutrality gray to the mobile/5G mass market. operators. It leverages 5G to create a new areas, like zero-rating. The good news is that independent of 5G, source of revenues through tiered pricing 4. Mobile users consume traffic transport networks are achieving new for connectivity services. Moreover, once and services on-the-fly and on-demand, levels of flexibility and software control these dynamic connectivity mechanisms making the network much more agile and that make dynamic allocation of resources are in place for 5G services, the telcos can dynamic by design. A mass market of 5G possible. This includes capabilities, such as extend this approach and associated users will use services intermittently. This dedicated queues for different traffic types, benefits to all mobile and fixed-access makes pooling of resources economically centralized traffic-engineered segment users. People will be able to enjoy viable and paves the way to creating routing, flexible allocation of hard resourc- high-definition video, lightning response various tiered service and connectivity es, such as optical channels, and sophisti- time for gaming, or experience real-time models. cated cloud-native SDN algorithms virtual reality, from wherever they happen 5. 5G’s architecture lends itself to (moving over time to AI/ML) to control all to be. resource pooling for dynamic services. The wireless “last mile” by definition uses a resource-pooling model, from the device eSIMs to the radio network, through the xHaul. Moreover, upgrading the fixed infrastructure for this last mile (to increase effective end-user speed from 100Mbps of 4G to 1Gbps of 5G, for example) is not overly expensive. Moving inwards from the RAN, the 5G architecture extends to distributed, Europe I | 2020 . 32
You can also read