Archana Venkateshan - Analytical services Chemist - Fat, Protein, Moisture, Ash, Dietary Fibre - Merieux NutriSciences
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
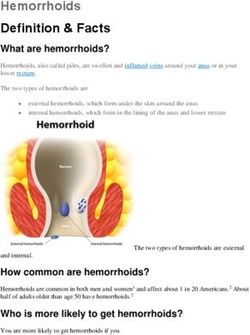
Proximates Testing – What & Why?
Fat, Protein, Moisture, Ash, Dietary Fibre
Archana Venkateshan - Analytical services Chemist
1
© Silliker Australia Pty Ltd 2017Speaker
Archana Venkateshan
Analytical services Chemist
Mérieux NutriSciences
© Silliker Australia Pty Ltd 2017Webinar Disclaimer
DISCLAIMER: Information presented on INFORM
presentations and webinars are for updates and
information purposes only. They do not constitute legal
advice or legal opinions. Mérieux NutriSciences Australia
makes no claims, promises or guarantees about the
accuracy, completeness or adequacy of the information
presented in this INFORM webinar.
© Silliker Australia Pty Ltd 2017MERIEUX NUTRISCIENCES CONNECT
A cost effective
integrated program of
leading scientific and
technical services
5CONTENTS
Why Multiple Methods for Each Test?
Moisture
Ash
Protein
Fat
Dietary Fiber
Calculation of Carbohydrates and
Energy
Conclusions
© Silliker Australia Pty Ltd 2017What Are Proximates?
Five categories:
Ash
1 main test method with 2 approaches
Moisture
3 main test methods
Protein
2 main test methods
Fat
3 main test methods
Some specific test methods
Fiber
crude fiber
Insoluble dietary fiber, Soluble dietary fiber
More accurate methods – Integrated DF
These results are used to calculate Carbohydrates & Calories
7What Do the Moisture Methods
Actually Measure?
Forced Air Oven Vacuum Oven Karl Fischer Titration
Evaporates Water Evaporates Water Measures water directly
8Moisture Method
Advantages/Disadvantages
Method Advantages Disadvantages
Forced Air- measures weight loss during Applicable to most foods & ingredients Not suitable for high sugar, volatile or
heating ( use of sand to increase surface are high fat foods due to > 100°C
and facilitate drying)
Fast (2-3 hrs), inexpensive, easy to Some foods require several hours
perform
Ovens = large capacity
Vacuum Oven- measures weight loss Inexpensive Longer test vs. Forced Air (3-5 hrs,
during heating sometimes overnight)
Vaccum allows lower temps to be used Vacuum maintenance system required
Some foods & ingredients misbehave at
higher temps
Example: high sugar foods carmelize
affecting results
Karl Fischer- measures water directly Good sensitivity, no heat required Longer test vs. Forced Air (3-5 hrs,
sometimes overnight)
Can distinguish moisture from non- Requires more sample preparation and
moisture volatiles (i.e. alcohol in a flavor titration skills. More expensive
concentrate) instrumentation and maintainence.
Method of choice for many low-moisture Reagents- safety, disposal concerns
foods or any low moisture food high in
sugar or protein.
9What Does the Ash Method
Actually Measure?
The analysis of ash content in foods is simply the burning away
of organic content, leaving inorganic minerals. This helps
determine the amount and type of minerals in
food; important because the amount of minerals can determine
physiochemical properties of foods, as well as retard the growth of
microorganisms.
Gentle Heating to Remove Water Combustion to remove
- Prevents Splattering all organic material
10The Ash Method
Measures the amount of non-organic material in the food by burning
away all the organic materials.
The remaining as are minerals as salts and oxides
As a hint: The %ash value is roughly 2X the amount of total metals
11What Do the Protein Methods
Actually Measure?
Kjeldahl Protein Method
ACID
&
Chemicals
Ammonia – a strong base
Total Nitrogen value Total Nitrogen measured
converted to %protein by titration with acid
12What Do the Protein Methods
Actually Measure?
Combustion (aka Dumas) Protein Method
Total Nitrogen value
converted to %protein
Total Nitrogen measured
directly
13The Different Protein Methods
Kjeldahl Protein
Converts all nitrogen to ammonia.
%Protein calculated using Protein Factors
Acceptable for nutritional labels
Combustion (Dumas) Protein
Converts all nitrogen to nitrogen molecules.
%Protein calculated using Protein Factors
Acceptable for nutritional labels
14The Different Protein Methods
Protein Factors
Converts %Total Nitrogen to %Protein.
KNOWING WHAT THE PROTEIN SOURCE IN THE FOOD IS
REQUIRED!
Default for mixed foods = 6.25. Dairy = 6.38. Wheat = 5.70.
There are other factors
Almonds 5.18
Barley, Oats, Wholemeal 5.83
Bran 6.31
Brazil nuts & Peanuts 5.46
Coconut & other tree nuts 5.30
Gelatin and Collagen 5.55
Rice 5.95
Whole eggs 6.68
15Protein Method Advantages /
Disadvantages
Kjeldahl Advantages Kjeldahl Disadvantages
Applicable to all foods Measures all organic nitrogen not just protein nitrogen
Most recognized method (around since 1883) Does not exclude economic adulteration agents (e.g.,
melamine)
Rapid methods routinely calibrated against this Corrosive reagents- some present disposal and safety
method concerns
Relatively simple, inexpensive Time consuming
Official crude protein method
Combustion Advantages Disadvantages
Applicable to all foods Measures all organic nitrogen not just protein
nitrogen
No toxic chemicals Does not exclude economic adulteration agents
(e.g., melamine)
Automation Increased speed and capacity,
Faster TAT*
Faster and easier to run
100% Nitrogen recovery
16What Do the Fat Methods
Actually Measure?
A
C triglycerides
I
D waxes
or esters
Base other ether-soluble stuff
Ether Extracted %Fat = most fat + some other stuff
Acid/Ether %Fat = all of the fat + more other stuff
Measure the amounts of all fatty acids
Mathematically express as “Fat”
%Fat = only the triglycerides (FDA “fat”) 17The Different Fat Methods (Core Methods?)
Soxhlet Fat
Measures the amount of surface fat and other ether-soluble stuff
Acid &/or Alkaline Digestion Fat Methods (Mojonnier Fat Methods)
Measure all the fat and more other ether-soluble stuff
This is the old FDA definition of fat
Can overestimate the %fat. Sometimes used on food labels since over-
declaring is allowed and this test is cheaper. Can also be used to justify
zero fat claims.
Ankom Fat analyser
It is automated Soxhlet analyser applicable for raw meats , minced
meats, pet foods , oil seeds and nuts.
18The Different Fat Methods (Core Methods?)
Fatty Acid Profile Fat Method
Measures only the triglycerides (current FDA definition of fat)
Required method for nutritional labels
Also measures each fatty acid separately
Saturated, Monounsaturated, Polyunsaturated and trans- Fatty Acids
We measure 37 fatty acid components using Gas chromatography
technique.
19What Do the Fiber Methods Actually Measure?
Dietary Fiber is what
arrives unchanged
into the large intestine
20Dietary Fiber Methods Advantages /
Disadvantages
Crude Fiber Dietary Fiber (AOAC 991.43)
Advantages Disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages
•Used as a quick •Does not simulate •Better simulates **Some highly-
test and for pet the human digestion human digestion soluble dietary fiber
foods system •Enzymes remove is missed by this
•Gives a good •**Not applicable to other carbs. Fat, method
estimate of %dietary nutritional labels ash, and protein are Fructooligosaccharides
(inulin), polydextrose,
fiber removed some resistant starches,
etc.
Codex Fiber (AOAC 2009.01 &
2011.25)
Advantages Disadvantages
•Much better **The method may
simulation of human miss some hydrolyzed
digestion FOS (aka liquid inulin
e.g.: includes 16 hr or liquid FOS).
enzyme digestion step
•Captures all dietary
fiber including
highly-soluble forms
21Important to Consider the Matrix
Critical for proper method selection- This is Why It is Important to Ask
Fat Methods
FAT_NH3
Fluid milk, dry milk, ice-cream, cream, cottage cheese, butter, water soluble samples
FAT_GRAVI
Cheese, butter, salad dressing, pet food, cereals, mixed entrees
FAT_ANKOM
Meat (raw and processed)
Oil seeds
Feeds
Nuts and nut butters
22Important to Consider the Matrix
Moisture Methods
MOIST-VO – 100
Total moisture in cheese, fluid dairy, dry dairy powders, syrups (DE < 58), grains
Moist-VO – 70 or 65
Free moisture in powders, sugars, syrups (DE > 58)
Karl Fischer
Samples with non-moisture volatiles (flavors with alcohol etc.)
23Carbohydrates
The amount of carbohydrates
declared on a label is not measured
directly.
ThePrinciple of Measuring
Carbohydrates
Measure all the non-carbohydrate
components
Subtract those values from 100%
The left-over amount is declared as
the amount of carbohydrates in the
food.
%Carbohydrates = 100% - %fat - %protein -%DF - %ash - %moisture
24Carbohydrates & Calories
Results from the Proximate tests are also used to calculate Energy
Energy (kJ /100g )= (Protein% x 17) + (Fat% x 37) + (Carbs% x 17) +
(DF% x 8 ) + (Alcohol% x 29)
Energy Value ( kcal/100 g ) = Energy Value ( kilojoules /100 g ) / 4.18
Note: 1 Cal is equivalent to 1 kcal
Yes, the calculated %carbohydrates does include vitamins, caffeine, and other
non-carbohydrates. The assumption is these levels are too small to matter.
25Non-Carbohydrates
What
are the non-carbohydrate
components?
Protein
Fat
Ash (minerals and salts)
Moisture
%Carbohydrates = 100% - %fat - %protein - %ash - %moisture
26Carbohydrates
When does the “By Difference” approach not work?
When the product contains non-carbs that are not protein, moisture, fat,
or ash.
Examples
Vitamins (in dietary supplements?)
Non-protein nitrogen gets counted as protein
The error of the 4 analytical results can be cumulative
Another approach for carbohydrate estimation is
Carbohydrate = Total starch +Total sugars
27Webinar program
Visit our website to have a look at our
webinar program and access our
webinar recordings and
presentations:
www.merieuxnutrisciences.com/au/digital-
solutions/mxns-inform-webinar
© Silliker Australia Pty Ltd 2017www.merieuxnutrisciences.com/au
Thank you for attending and interacting today.
Please contact us:
For sales enquiries at: sales.au@mxns.com
For webinar information at: marketing.au@mxns.com
© Silliker Australia Pty Ltd 2017You can also read