Come colpire il reservoir di HIV durante l'infezione acuta? Isabella Abbate, Ph.D. Laboratory of Virology INMI "L. Spallanzani" - Rome - Italy ...
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Come colpire il reservoir di HIV durante l’infezione acuta?
Il punto di vista del virologo
Isabella Abbate, Ph.D.
Laboratory of Virology
INMI “L. Spallanzani” - Rome - Italy
Dr. I. Abbate has no financial relationships with commercial entities to discloseEarly treatment, HIV Remission, Functional cure
PLOS Pathogens | www.plospathogens.org 1 March 2013 | Volume 9 | Issue 3 | e1003211The rapidity of viral rebound after cART discontinuation is
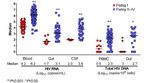
associated with the size of HIV reservoirTwo phases of HIV DNA decay both more pronuonced in PHI as compared to CHI, at the end of follow-up (median of 4 yrs viral suppression) HIV DNA lower in PHI
AIDS 2017, 31:477–484
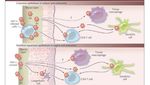
Timing of reservoir seeding during acute infection:
from HIV-1 transmission to productive clinical infection
Modified from Cohen MS et al.
N Engl J Med 2011Come colpire il reservoir durante l’infezione acuta? (Il punto di vista del Virologo) ….con una diagnosi più precoce possibile nel contesto di una strategia di “Test and treat” (dallo START study 2015)
HIV diagnosis
Classificazione infezioni acute/recenti secondo Fiebig
Original article: Fiebig et al. Staging system for primary HIV infection, AIDS 2003
Cumulative duration
(days)
eclipse: 10 (7-21)
I 7 (13-28)
II 22 (18-34)
III 25 (22-37)
IV 31 (27-43)
V 101 (71-154)
VI open ended
From: McMichael AJ, Borrow P, Tomaras GD, Goonetilleke N, Haynes BF
The immune response during acute HIV-1 infection: clues for vaccine development, Nature Reviews Immunology 2010CID 2018:66 (15 May) •
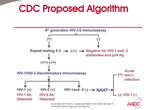
NAT are not recommended for initial HIV screening because, while they offer a marginal advantage over fourth generation screening assays in detecting recent infection, they are not licensed for diagnostic use and may give false- positive results
Updated January 2018 Pandori ed al: Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010
Schematic representation of the 30-year evolution of HIV
diagnostic assays.
Thomas S. Alexander Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016;23:249-
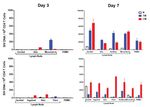
253SIREA Study at INMI L.Spallanzani Rome (0C9 Virology)
119 PHI patients from Lug 2013 to Mar 2018 (93%M; mean age 35y; 74.6% MSM)
FII=10, FIII=11, FIV=29, FV=34 and FVI=35.
At baseline, plasma HIV-1 RNA and HIV-1 DNA showed a similar trend during the different phases of primary infection
with median values higher in early as compared to recent infections. CD4 T cell counts were lower in E as compared to
R infections, CD4/CD8 ratio showed no differences between the two groupsAIDS 2015, 29:793–800
The Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre anonymous HIV voluntary counseling and testing center
RV254/SEARCH 010 offering immediate ART to patients
Among 74 334 clients screened for HIV infection, HIV
prevalence was 10.9% and the overall incidence of AHI
(N=112) was 2.2 per 100 person-years.
The inclusion of pooled NAT in the testing algorithm increased
the number of acutely infected patients detected, from 81 to
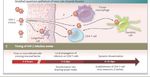
112 (38%), relative to 4thG HIV antigen/antibody immunoassay.HIV reservoir during the different phases of primary infection
Ananworanich et al. Retrovirology 2013, 10:56Semiannual HIV screening via fourth-generation immunoassay is a better use of resources than annual pooled NAAT. Pooled NAAT testing every 12 months of MSM and IDUs in the United States prevents a modest number of infections, but may be cost-effective given sufficiently high HIV prevalence levels. Reduces incidence by 9.6% and costs 92000$ per QALY gained Remains 4% However, testing via fourth-generation immunoassay every six months prevents a greater number of infections, is more economically efficient, and may obviate the benefits of acute HIV screening via NAAT. Reduces uncidence by 16% and costs
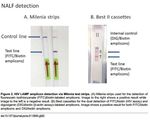
Point of care test (POC) One of the challenges to infectious disease diagnosis in low-resource settings (LRS) is that many infections occur far away from centralized laboratories where diagnostic tests are routine. Unfortunately, few diagnostic tests can be performed in LRS. In response to the need for improved diagnostic tests for the developing world, the World Health Organization (WHO) Sexually Transmitted Diseases Diagnostics Initiative (SDI) has identified appropriate diagnostic test attributes to address disease control needs for LRS. These attributes, refered to as the “ASSURED” criteria can be summarized as: sensitive, specific, user-friendly, rapid and robust, equipment-free and deliverable to end-users.
4° Gen POC
PLOS ONE | DOI:10.1371/ 2016
Fitzgerald N, et al. Sex Transm Infect 2017;93:100–101.NAT POC
Cobas Liat Roche
GeneXpert® HIV-1
Qual assay
SAMBA HIV qualitative TestPLOS ONE | DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0113693 November 26, 2014
NAT POC
Non-instrumented nucleic acid
amplification (NINA) devices that
generate heat from the exothermic
reaction of calcium oxide and water
For a recent review on miniaturized devices for POC molecular detection of HIV see:
Mauk et al Lab Chip 2017, 17:382.Journal of the International AIDS Society 2017, 20: 21579
You can also read