How's Life in Korea? - OECD
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
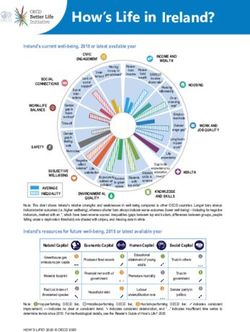
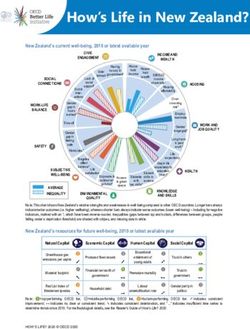
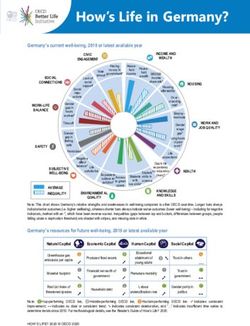
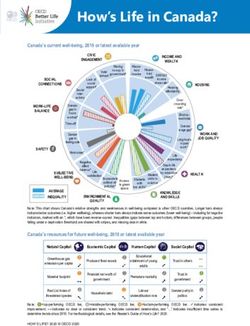
How’s Life in Korea?
How’s Life in Korea?
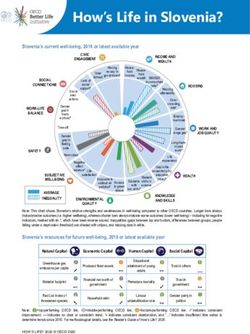
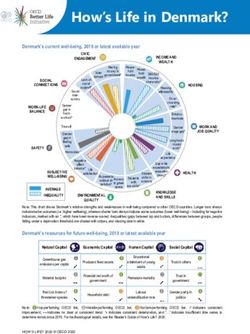
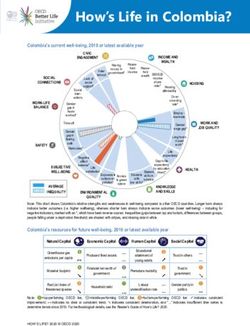
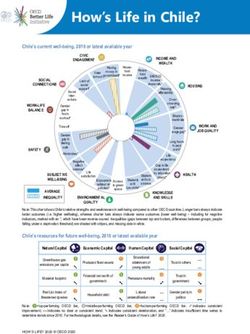
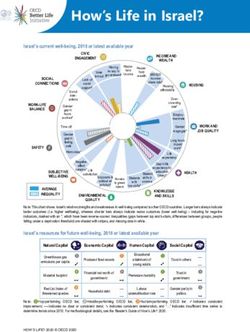
Korea’s current well-being, 2018 or latest available year
CIVIC
INCOME AND
ENGAGEMENT
WEALTH
Hav ing House-
no say in hold House-
Voter
income hold S80/S20
turnout gov ernment* w ealth income
SOCIAL Lack of
share ratio*
CONNECTIONS social HOUSING
support* Housing
Social affordability
inter-
actions Ov er-
WORK-LIFE crow ding
Gender rate*
BALANCE gap in
hours
Employ -
w orked*
ment rate
Time off
Gender WORK AND
w age gap* JOB QUALITY
Gender
gap in
feeling Long hours
safe in paid
SAFETY w ork*
Homicides*
Life
Negativ e ex pectancy
affect Gap in life
balance* Life ex pectancy by
SUBJECTIVE satisfaction Student education HEALTH
WELL-BEING Ex posure to Access Students skills in (men)*
outdoor air to green w ith science
pollution* space low skills*
AVERAGE
KNOWLEDGE
INEQUALITY ENVIRONMENTAL AND SKILLS
QUALITY
Note: This chart shows Korea’s relative strengths and weaknesses in well-being compared to other OECD countries. Longer bars always indicate
better outcomes (i.e. higher wellbeing), whereas shorter bars always indicate worse outcomes (lower well-being) – including for negative
indicators, marked with an *, which have been reverse-scored. Inequalities (gaps between top and bottom, differences between groups, people
falling under a deprivation threshold) are shaded with stripes, and missing data in white.
Korea’s resources for future well-being, 2018 or latest available year
Natural Capital Economic Capital Human Capital Social Capital
Educational
Greenhouse gas
Produced fixed assets attainment of young Trust in others
…
emissions per capita
adults …
Financial net worth of Trust in
Material footprint Premature mortality
government government
Red List Index of
Household debt
Labour … Gender parity in
threatened species underutilisation rate politics
…
Note: ❶=top-performing OECD tier, ❷=middle-performing OECD tier, ❸=bottom-performing OECD tier. ➚ indicates consistent
improvement; ↔ indicates no clear or consistent trend; ➘ indicates consistent deterioration, and “…” indicates insufficient time series to
determine trends since 2010. For methodological details, see the Reader’s Guide of How’s Life? 2020.
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 20202
For more information
Access the complete publication, including information about the methods used to determine trends at:
https://doi.org/10.1787/9870c393-en.
Find the data used in this country profile at: http://oecd.org/statistics/Better-Life-Initiative-2020-country-
notes-data.xlsx.
Deprivations in Korea
Deprivations in selected indicators of current well-being, 2018 or latest available year
KOREA
17% 4%
of the population live in relative would be at risk of falling into poverty if they
income poverty had to forgo 3 months of their income
9% 12%
of poor households spend more than of the population report low
40% of their income on housing costs life satisfaction
19%
say they have no friends or family There is no data available on satisfaction
to turn to in times of need with time use
Source: OECD (2020), How’s Life? 2020: Measuring Well-Being
Note: Relative income poverty refers to the share of people with household disposable income below 50% of the national median; financial
insecurity refers to the share of individuals who are not income poor, but whose liquid financial assets are insufficient to support them at the
level of the national relative income poverty line for at least three months; housing cost overburden refers to the share of households in the
bottom 40% of the income distribution spending more than 40% of their disposable income on housing costs; and low satisfaction with life and
with time use refer to the share of the population rating their satisfaction as 4 or lower (on a 0-10 scale).
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 20203
Inequalities between men and women in Korea
Gender ratios (distance from parity) for selected indicators of current well-being, 2018 or latest available year
Earnings 0.65
Employment rate 0.73
Feeling safe 0.74
Perceived health 0.76
Long-term
unemployment rate
0.90
Hours worked
(paid and unpaid)
0.95
Time off 0.96
Adult skills (numeracy) 0.96
Student skills (science) 0.99
Life satisfaction 1.03
Social support 1.05
Life expectancy 1.08
Having a say in
government
1.12
Homicide victims 1.13
Social interactions 1.22
Job strain 1.24
Deaths from suicide,
alcohol, drugs
// 2.79
Men doing better OECD average Women doing better
Note: Grey bubbles denote no clear difference between men and women, defined as gender ratios within 0.03 points distance to parity.
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 20204
Inequalities between age groups in Korea
Age ratios (distance from parity) for selected indicators of current well-being, 2018 or latest available year
A. Younger and middle-aged people
Employment rate // 0.34
Earnings 0.67
Voter turnout 0.77
Job strain 0.86
Feeling safe 0.98
Life satisfaction 0.98
Adult skills (numeracy) 1.02
Social support 1.16
Having a say in
government
1.28
Long-term
unemployment rate
// 3.09
Middle-aged people doing better OECD average Younger people doing better
B. Younger and older people
Long-term
unemployment rate
// 0.16
Employment rate // 0.39
Voter turnout // 0.55
Earnings 0.74
Feeling safe 0.89
Life satisfaction 1.02
Job strain 1.04
Adult skills (numeracy) 1.15
Social support // 1.48
Having a say in
government
// 1.74
Older people doing better OECD average Younger people doing better
Note: Age ranges differ according to each indicator and are only broadly comparable. They generally refer to 15-24/29 years for young people,
25/30 to 45/50 years for the middle-aged and 50 years and over for older people. See How’s Life? 2020 for further details. Grey bubbles denote
no clear difference between age groups, defined as age ratios within 0.03 points distance to parity.
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 20205
Inequalities between people with different educational attainment in Korea
Education ratios (distance from parity) for selected indicators of current well-being, 2018 or latest available year
Job strain // 0.29
Earnings 0.67
Perceived health 0.73
Having a say in
government
0.83
Feeling safe 0.86
Employment rate 0.93
Social support 0.95
Life satisfaction 0.97
Voter turnout 1.08
People with tertiary education doing better OECD average People with upper secondary education doing better
Note: Grey bubbles denote no clear difference between groups with different educational attainment, defined as education ratios within
0.03 points distance to parity.
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 20206
Inequalities between top and bottom performers in Korea
Vertical inequalities for selected indicators of current well-being, 2018 or latest available year
Household income of the top 20% relative to the bottom 20% Share of wealth owned by the top 10%, percentage
12 90
80
10
70
8 60
7 51.7
50
6 5.4
40
4 30
20
2
10
0 0
Earnings of the top 10% relative to the bottom 10%, PISA score in science of the top 10% relative to the bottom 10%
full-time employees
6 2
1.67 1.66
5
4.3
4
3.4
3 1
2
1
0 0
Life satisfaction scores of the top 20% relative to the bottom 20% Satisfaction with time use scores of the top 20%
relative to the bottom 20%
4 4
3 3 2.78
2.2 2.1
2 2
1 1
0 0
Note: For all figures, countries are ranked from left (most unequal) to right (least unequal).
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 20207
Trends in current well-being since 2010 in Korea - I
Household income
(household net adjusted disposable income, Average
KOR OECD
USD at 2017 PPPs*, per capita) ~24 000 ~ 28 000
Income and Wealth
Household wealth
Average
(median net wealth, USD at 2016 PPPs) OECD KOR
~162 000 ~173 000
S80/S20 income share ratio
(the household income for the top 20%,
Inequality
divided by the household income for the KOR OECD
bottom 20%) 7 5.4
Housing affordability
(share of disposable income remaining after Average
OECD KOR
housing costs) 79.2 84.8
Housing
Overcrowding rate
(share of households living in overcrowded Inequality KOR
OECD
conditions) 12 8
Employment rate
(employed people aged 25-64, as a share of Average
the population of the same age) KOR OECD
74.1 76.5
Work and Job Quality
Gender wage gap
(difference between male and female median Inequality
wages expressed as a share of male wages) KOR OECD
34.6 12.9
Long hours in paid work
(share of employees usually working 50+ Inequality No data available for Korea
hours per week)
Life expectancy
Health
(number of years a newborn can expect to Average
live) OECD KOR
80.5 82.7
Note: The snapshot depicts data for 2018, or the latest available year, for each indicator. The colour of the circle indicates the direction of
change, relative to 2010, or the closest available year: = consistent improvement, = consistent deterioration, = no clear trend,
and white for insufficient time series to determine trends. The OECD average is marked in black. For methodological details, see the Reader’s
Guide of How’s Life? 2020. * = Purchasing Power Parity.
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 20208
Trends in current well-being since 2010 in Korea - II
Environmental Knowledge and
Student skills in science
Skills
Average
(PISA mean scores) OECD KOR
489 519
Quality
Exposure to outdoor air pollution
Inequality
(share of population > WHO threshold)
KOR OECD
99.2 62.8
Life satisfaction
Subjective Well-being
Average
(mean value on a 0-10 scale)
KOR OECD
6.1 7.4
Negative affect balance
(share of population reporting more negative Inequality
than positive feelings and states yesterday) KOR OECD
17 13
Homicides
Average
(per 100 000 population) OECD KOR
2.4 0.9
Safety
Gender gap in feeling safe
(percentage difference that women feel less Inequality
safe than men when walking alone at night) KOR
OECD -15.8
-16
Time off
Work-life
Balance
(time allocated to leisure and personal care, Average
hours per day) KOR OECD
14.8 15
Social interactions
Average
Social Connections
(hours per week)
KOR OECD
4.9 6
Lack of social support
(share of people who report having no friends
Inequality
or relatives whom they can count on in times
KOR OECD
of trouble) 19.2 8.6
Engagement
Voter turnout
Civic
Average
(share of registered voters who cast votes) OECD KOR
69 77
Note: See note on page 7.
HOW’S LIFE? 2020 © OECD 2020You can also read