North American Bitcoin Mining Index (NABMI) - A comprehensive analysis of the companies, capital, and energy mix powering Bitcoin mining in North ...
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
1
North American
Bitcoin Mining
Index (NABMI)
A comprehensive analysis of the
companies, capital, and energy mix
powering Bitcoin mining in North America2
North American Bitcoin Mining
Index (NABMI)
A comprehensive analysis of the companies, capital, and ener-
gy mix powering Bitcoin mining in North America
By John Lee Quigley3
Acknowledgements
Apolline Blandin • Leo Zhang • Shaun O’Connell • Samson Mow • Amanda Fabiano
Drew Armstrong • AJ Scalia • Kevin Zhao • Nathan Nichols • Harry Sudock • Steve Barbour
Sam Doctor • Karth Potluri • Yuriy Blokhin • Scott Howard • Jurica Bulovic • Ethan Vera
Wes Fulford • Rich Godwin • Jason Les • Trevor Smyth • Karim Helmy • Brian Wright
Taras Kuylk • Alexander Barnes • Jaran Mellerud
Index
Foreword – 4 Chapter 2. Can United States Miners Compete at the
Introduction – 6 Same Scale as Chinese Miners – 26
Methodology and Future Research – 7 • The Paradigm Shifts of Bitcoin ASIC
Chapter 1. The United States Bitcoin Mining Industry Manufacturing – 26
–8 • Greater Block Rewards Market Spurs
• Growth of Bitcoin Mining in the United First Major Shift – 27
States, Infrastructure Play, Jurisdictional • Second Major Shift Approaching – 27
Certainty, and Institutional Presence – 8 • Hardware Lifecycles Lengthening
• US Regulatory Developments – 8 Dissipate Chinese Advantage – 28
• High Degree of Jurisdictional • Factors Beyond Hardware – 29
Certainty – 9 • Jurisdictional Certainty – 30
• The Double-Edged Sword of the US • Competitive Cost Structures – 30
Capital Markets – 10 • Seasonality and Migration Costs 30
• Cheap Financing Increases • Chapter 2 Summary – 31
Valuations – 11 Chapter 3. The Canadian Bitcoin Mining Industry –32
• Public Versus Private – 11 • Canada’s Cryptocurrency Industry – 33
• Burgeoning Financial Services – 12 • Electricity Markets – Inexpensive Power
• US versus Overseas – 12 Prices Meet Scalability Restrictions – 34
• The History of Hardware in the United States • Canada’s Bureaucratic Regulatory
– 13 Environment – 36
• Hardware Market Characteristics –13 • An Easier Route to the Public Markets – 38
• Historical Hardware Procurement • Hardware Importation, Climate Conditions,
Difficulties Facing US Miners – 16 and Domestic Currency Strength – 40
• Hardware Manufacturer • Chapter 3 Summary – 41
Institutionalization – 17 Conclusion – 42
• The Complexity and Opportunity in the US Bibliography – 43
Energy Market – 18
• Sourcing Energy in the US Electricity
Market –18
• ERCOT Cost Breakdown and
Demand-Response Programs – 19
• Bitcoin Mining in New York - 21
• Bitcoin Energy Consumption
Concerns – 22
• Exploring Underutilized and
Stranded Energy – 23
• The Emergence of the Energy Sector
– 24
• Chapter 1 Summary – 254
North American Bitcoin
Mining Index (NABMI)
A comprehensive analysis of the companies, capital, and
energy mix powering Bitcoin mining in North America
Foreword
North America is emerging as a serious contender to Energy tends to be the most costly and perhaps the
house the largest Bitcoin mining industry in the world. most important input for miners. While the average
China has historically been home to the dominant energy price is still higher for North American miners
share of the industry with hashrate production and than miners in the Asia-Pacific, the United States and
mining pools heavily concentrated in the region. Their Canada are rich with both fossil fuels and renewable
dominance has been partly driven by their control of energy sources, providing significant opportunities to
Bitcoin ASIC manufacturing. Chinese miners have entrepreneurial mining operators. At scale, large min-
historically benefited from shorter delivery times and ers can source globally competitive electricity rates for
preferential access to hardware, but the dynamics of the hundreds of megawatts of capacity. At a smaller scale,
global industry are shifting. promising young companies are democratizing and de-
centralizing mining by bringing energy producers into
Compass Mining’s dive into the growth of the Bitcoin the industry through deployments of shipping-con-
mining industry in North America highlights that tainer-style mobile “data centers” at points of wasted or
miners are placing greater emphasis on jurisdictional stranded energy. There is potential for scale here, as the
certainty, long-term access to inexpensive power pric- U.S.’s 2019 output of 538 billion cubic feet of vented and
es, and the opportunity to establish operations that can flared natural gas could alone power all North Ameri-
be competitive for multiple decades. They are willing can miners many times over [1]. These young compa-
to forgo the advantages of preferential hardware de- nies are creating solutions to manage energy loads that
livery times to set up structures that they believe can simultaneously increase revenues by monetizing sur-
give them a sustainable competitive advantage in an plus energy, reduce waste, and provide a more reliable
industry where inefficiency rarely survives. The narra- energy supply for down-stream consumers.
tive that China could potentially influence Bitcoin may
therefore naturally subside if China’s relative domi- North America’s energy supply is a strong natural ad-
nance over mining declines with the growth of the vantage, but North America’s biggest competitive edge
North American Bitcoin mining industry. could be its robust capital markets. North American
miners have access to unmatched quantities of capital
Several trends and natural competitive advantages sug that have facilitated hundreds of millions of dollars in
gest that North America will continue to increase its hardware purchases. Estimates suggest North Amer-
total hashrate and may eventually compete with Chi- ican miners have purchased at least $500 million in
na for the largest share of global network hashrate. As hardware over the last year, which may be conservative
Bitcoin continues to permeate through our society, we as it only accounts for the public announcements [2].
are noticing a clear corresponding increase in talent This flow of capital into the industry is critical since
and innovators entering the Bitcoin ecosystem. Within Chinese miners have a competitive edge in their ability
Fidelity’s Center for Applied Technology (FCAT), we to acquire hardware at a lower price point than their
are optimistic about North American mining partly North American counterparts. As institutional inves-
because of this surge in passionate talent dedicating tors allocate more capital towards Bitcoin mining, there
their talent to its growth. We are already witnessing the is also a greater need for sophisticated risk manage-
results through impactful innovations across energy ment strategies. Although we are still early, the finan-
infrastructure, financial instruments, and technology cialization of mining is a clear trend, and we are already
aimed specifically at helping miners grow. seeing innovation in derivatives and other investment5
products that are evolving from early-stage concepts are still in the early days of tapping into its potential to
to live products with real volumes. The assurance to support miners. It is time-intensive to build facilities
capital allocators that familiar risk management prod- that can support hundreds of megawatts of capacity, so
ucts and strategies are becoming available may increase even those receiving funding today may not come on-
their willingness to invest in the space. line for years.
Despite accelerating growth, the North American min- There is good reason to be optimistic about the future
ing industry still faces challenges. Hardware procure- of Bitcoin mining in North America. Unfortunate-
ment is among the greatest challenges for miners glob- ly, much of the information on the state of mining in
ally, but it is of particular concern to North American North America is still misrepresented, fragmented,
miners who are geographically isolated from points of and incomplete. The following report from Compass
production in Asia and must add import costs onto the covers the trends I have mentioned above and more,
hardware price. This is among the most significant bar- providing the most comprehensive overview of Bitcoin
riers to achieving greater geographic hashrate disper- mining in North America to date. Reports like these
sion. North America is far behind Chinese ASIC man- are critical to educating a largely uninformed pub-
ufacturers and catching up would require substantial lic about the current state of mining in the West and
capital and time. Although this Compass report out- North America’s opportunity to challenge the incum-
lines reasons to be optimistic about the state of hard- bents. Turning what has traditionally been an opaque
ware procurement in North America, this challenge and walled-off industry into one that is transparent
will likely persist for many years. and accessible is critical to the industry’s maturation,
and Compass is among the leaders in driving towards
Apart from hardware, and despite the impressive that end. We at the Fidelity Center for Applied Tech-
growth I’ve mentioned, there are also still many phys- nology thank Compass for contributing such strong
ical and network infrastructure needs. It is not until research to the public and hope that reports like
quite recently, for example, that North American min- these will become more common in a dynamic and
ers had the option to contribute hashrate to institution- promising industry.
al-quality pools based in North America. Until Ameri-
can pools can compete in size with those in China, it is — Brian Wright, Director, Bitcoin Mining
likely that narratives of China’s control over Bitcoin will Fidelity Center for Applied Technology
persist. Furthermore, although North American ener-
gy infrastructure is a strong competitive advantage, we6
Introduction
The dominant share of the Bitcoin mining market has recent trend towards Bitcoin mining becoming a more
resided in China since its genesis in 2013. All mass- institutionalized activity in the US. Significant sections
scale Bitcoin ASIC hardware manufacturers are based are dedicated to understanding the country’s capital
in China while Bitcoin mining service providers and markets and electricity markets and how they pertain
Bitcoin mining pools are also heavily concentrated in to Bitcoin miners. The Texas ERCOT market is closely
the country. Recent estimates place China’s share of examined and we consider the effective power prices
hashrate production between 40% and 60% [4]. that miners can secure by participating in demand-re-
sponse programs in this market. A significant section
The landscape is changing though as North America’s is also dedicated to understanding the conditions US
Bitcoin mining ecosystem continues to grow at a fast miners face when procuring hardware.
pace. Not only are pure-play miners bringing more
hashrate onshore but service providers, mining pools, Chapter 2 considers whether the US Bitcoin mining
and startups with innovative concepts are all emerging industry can grow to the same scale as the Chinese Bit-
with the imperative of establishing long-term opera- coin mining industry. This chapter will provide further
tions in North America. detail on China’s historic dominance in the mining in-
dustry while also highlighting its previous dominance
This report explores the evolving nature of the Bitcoin of bitcoin-fiat trading volume. Hardware has been a
mining industry and how North America, and the US defining factor that has maintained China’s foothold
in particular, are positioning themselves to become the over the Bitcoin mining industry. We dedicate the
leading Bitcoin mining industry. We will analyze the majority of this chapter to analyzing how the Bitcoin
key factors underpinning the growth in the US Bitcoin ASIC manufacturing industry has evolved historical-
mining industry and also consider developments that ly and how it is likely to change moving forward. We
have changed the favorability of mining in China. We consider how these changes impact the relative advan-
will also review the Bitcoin mining industry in Canada tages of mining in the US compared to China. We also
and the relative tradeoffs of mining in the country. The consider factors like weather seasonality and the im-
study is split into three chapters. pact on power prices, data center buildout costs, and
jurisdictional certainty.
This report does not include research on the state of
Bitcoin mining operations in Mexico or other Latin Chapter 3 details the Bitcoin mining industry in Cana-
American nations, due to the relative youthfulness of da, an industry that burgeoned earlier than the US and
mining markets in those areas compared to both the is home to a mixture of cryptocurrency-related com-
US and Canada. They are a favorable choice for fu- panies. Canadian miners have the possibility to secure
ture research, particularly given recent attention in some of the most attractive power prices across North
El Salvador. America but also face a more bureaucratic regulatory
environment that can restrict scalability and impose
Chapter 1 details the Bitcoin mining industry in the additional costs. Before presenting the three chapters,
US. The chapter includes an overview of some of the we will outline how the study was carried out in the
main players in the US ecosystem and highlights the methodology section.7
Methodology and Future Research
The North American Bitcoin Mining Index study con- A thorough literature review was conducted which
sisted of the following research activities: (1) An explo- provided independent information for the report. The
ration process where the research question that the re- literature review further served to corroborate or refute
port aimed to address was determined. This was mainly information retrieved during the interview process.
determined through a mixture of online research, dis- Over 1500 sources from media outlets, press releases,
cussions with fellow researchers, and discussions with government agencies, previous research studies, social
industry professionals, (2) A collection of unstructured media posts, and interviews were examined during
phone interviews with industry professionals who are this process.
active in the North American Bitcoin mining industry.
(3) A literature review to assess the current informa- Data analysis was carried out on: (i) the relationship
tion available on the Bitcoin mining industry in North between Bitcoin price and the secondary market hard-
America. The literature review further served to cor- ware prices of both latest-generation and old-genera-
roborate or refute the information retrieved during the tion mining equipment, (ii) the historical size of the
interview process. (4) Independent data analysis. Anal- annualized block subsidy market. Data for hardware
ysis was carried out on third-party data to draw further prices was sourced from hashrateindex.com while the
insights. (5) Peer review. The final document was for- Bitcoin price data was sourced from the daily closing
warded to individuals for critique and input. price of the BitMEX perpetual Bitcoin contract [5].
The BitMEX perpetual Bitcoin contract was used be-
Seventeen industry professionals were interviewed as cause its price is derived from the price of several Bit-
part of the research process. Each conversation lasted coin spot exchanges, giving a more representative in-
roughly one hour and was unstructured. Before each dication of the broader Bitcoin market, compared to a
interview, research was carried out on the interview- single exchange which can be subject to instances of
ee and prospective questions were drawn. Interview- illiquidity [6]. The correlation between hardware prices
ees were primarily founders and C-level executives of and Bitcoin price along with the associated graphs were
North American mining-related companies. The inter- derived from Google Sheets. The graph associated with
viewees included professionals from companies with the historic size of the annualized block subsidy market
activities related to proprietary mining, mining pools, was generated in a Jupyter Notebook using the Python
infrastructure, financial services, and energy. One pro- Plotly library.
fessional was interviewed twice and one professional
was interviewed four times to clarify and expand upon The final draft of the study was forwarded to colleagues,
certain areas. Notes were taken during the interview, industry professionals, researchers, and other indi-
and these notes, combined with the literature review, viduals familiar with the Bitcoin mining industry for
formed the primary basis for this report’s information. critique and feedback. Several suggestions were made
No specific quotes were included from the interviews. during this process and the research report was appro-
Any quotes included in the research report were refer- priately adjusted.
enced from publicly available sources.8
Chapter 1
The United States Bitcoin Mining Industry
Several factors foster favorable conditions for mining in the US, leading many industry professionals to anticipate
that it is only a matter of time before the US claims the largest share of hashrate production. Having the biggest
capital markets in the world have played a considerable role in the growth of the US Bitcoin mining industry.
The capital raising ability of US companies has allowed them to compete intensely for a limited share of hard-
ware supply coming on to the market. Hardware is the key constraint facing miners globally. Upon establishing
competitive cost structures, it is an imperative of miners to maximise their output. However, hardware limits the
ability to expand. We will detail the dynamics of the hardware market and how it has evolved since the early stages
of the industry.
A complex but abundant power market has provided opportunities to procure extremely low-cost energy that can
place US miners among the lowest-cost miners in the industry. The Texas market is among the most attractive
regions for miners securing low-cost energy and it is anticipated that a power law will form where the majority of
hashrate production is generated within these regions. Chapter 1 will discuss all of these factors in further detail
and present an overview of the current advantages and disadvantages facing US Bitcoin miners.
Growth of Bitcoin Mining in the United States, Infrastructure Play, Jurisdictional Certainty,
and Institutional Presence
Data suggests that the US mining industry has record- established operations in the United States Bitcoin
ed a phase of immense growth since September 2019 mining industry. Several mining-focused companies
[7, 8]. This growth is corroborated by a growing insti- have publicly listed in the United States and companies
tutional presence. Entities like Fidelity Center for Ap- are emerging with a focus on providing various ser-
plied Technology (FCAT), Galaxy Digital, and Digital vices to the industry.
Currency Group are among the institutions that have
US Regulatory Developments
Recent regulatory developments in the United States We therefore conclude that a bank may validate, store,
indicate an increased interest in blockchain technology and record payment transactions by serving as a node
from the US government. The Office of the Comptrol- on an INVN. Likewise, a bank may use INVNs and re-
ler of the Currency (OCC) issued several interpretive lated stablecoins to carry out permissible payment ac-
letters that have elucidated how banks can interact tivities.” (Interpretive Letter #1174, OCC)
with the technology. These letters have served to clarify
the following: In December 2020, a proposal by the US Treasury
near the end of the Trump administration attempted
• Banks can custody cryptocurrencies and stablecoins to secure oversight into the Bitcoin network, similar
(Interpretive Letter #1170) [11]. to the oversight that is exercised in the banking sec-
tor. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (Fin-
• Banks can treat blockchains as a settlement infrastruc- CEN), a department within the US Treasury, sought
ture. Banks can use stablecoins to facilitate payments to impose know-your-customer (KYC) requirements
on behalf of customers (Interpretive Letter #1174) [12]. on cryptocurrency exchanges for transactions relat-
ing to self-hosted wallets [13]. Specifically, the rule
“INVNs [Independent Node Verification Network] and would require carrying out KYC on self-hosted wallets
related stablecoins represent new technological means and would require exchanges to store data for trans-
of carrying out bank-permissible payment activities. actions greater than $3,000. For transactions greater9
than $10,000, the rule would require exchanges to re- While comments from the US government specifically
port the information to FinCEN. The rules would give related to Bitcoin mining are sparse, Brian Brooks, For-
FinCEN similar oversight to what they exercise in the mer Acting Comptroller of the Currency at the OCC,
bank sector through the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). The stated in an interview that the United States faced a
proposal received backlash from entities operating in “geo-strategic competitiveness” issue due to the large
the industry for several reasons. Onerous reporting re- share of mining infrastructure residing in China [14].
quirements and privacy infringement concerns were Such sentiment combined with the entry of large-scale
among the critiques. Square and Coinbase were among institutions into the United States industry, and their
the companies that criticized the proposal. The propos- respective tax dollars, place Bitcoin mining firmly in
al was discontinued under the Biden administration. the interests of the US government. We will likely ob-
serve greater commentary on the industry from gov-
ernment authorities in the proceeding years.
High Degree of Jurisdictional Certainty
One of the factors driving a migration of hashrate to the 1st of March, BitOoda’s Chief Strategy Officer Sam
the US is a high degree of confidence in how juris- Doctor commented that part of the motive could be to
dictions will treat the Bitcoin mining industry. Harry close the ability of Bitcoin miners to circumvent capital
Sudock, VP of Strategy at Griid Infrastructure, noted controls. Doctor anticipates that we may observe such
“jurisdictional certainty” as one of the key variables bans extending to other Chinese regions.
providing favorable conditions for mining in the US
[15]. Sudock elaborated that clarity surrounding tax Other jurisdictional decisions in China have followed,
treatment, energy treatment, and tariff regimes helps with Bitcoin mining being banned or curtailed in both
make the US a region where multi-decade businesses Xinjiang and Qinghai provinces in early June 2021
can be established. In contrast, miners operating in [155,156].Miners were also instructed to follow new
China face much more uncertain jurisdictional condi- regulations in Yunnan province the same month, in-
tions. Chinese miners have been noted to operate in cluding registering with local authorities [157].
a “legal grey area, with large differences in treatment
between local jurisdictions’’ [16]. It has been noted in Previous research has highlighted how the properties
the literature as early as November 2018 that Chinese underpinning the Bitcoin network juxtapose the struc-
miners were either leaving the country or choosing not ture and practice of the Chinese government, making
to reinvest in domestic operations. On a separate occa- efforts to curb mining activities more likely in the re-
sion, Sudock commented that Chinese miners “do not gion [19]. The Chinese government has implemented
live under a stable regulatory regime” [4]. widespread censorship of information, through what
is popularly known as the “Great Firewall of China”
This view has been corroborated by recent develop- [20]. This censorship contrasts the censorship-resistant
ments in China’s Inner Mongolia region. On February and politically agnostic nature of the Bitcoin network.
25th, Inner Mongolia’s Development and Reform Com- Moreover, Bitcoin’s permissionless payments provide
mission (DRC), proposed a regulation to shut down all a route for Chinese citizens to circumvent the capital
cryptocurrency mining facilities in the region [17]. The controls imposed by the government.
Inner Mongolia DRC is a local branch of the country’s
National Development and Reform Commission, one In contrast, the US is a jurisdiction that can provide a
of the Chinese government’s 26 cabinets which is re- high degree of clarity around business activities where
sponsible for regulating economic activities on a local sudden aggressive changes in regulation are much more
level. The proposal aims to fully “clear out and shut unlikely. The imperative of some US mining companies
down all virtual currency mining projects by the end to comply with existing regulations is a positive for
of April 2021” [18]. The proposal is currently receiving how mining-related regulations might evolve moving
public feedback. Efforts to constrain annual growth in forward. Some mining pools confirmed that they have
energy consumption to 1.9% was the stated motive for carried out KYC on their connected miners while also
the regulation proposal. In a newsletter published on investigating their payout addresses to ensure that the10
addresses are unconnected with any addresses associ- their operational headquarters. Luxor Mining, DMG,
ated with illicit activities. DMG and Marathon Group Foundry, and Titan will all provide mining pool ser-
contentiously took this a step further by launching a vices that primarily target US-based miners. Since the
pool that actively censors transactions that are not start of 2016, almost all of the Bitcoin hashrate has been
compliant with rules set forth by the US Government’s connected to mining pool entities that have their oper-
Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) [21]. Mara- ational headquarters in China [22]. Braiins is a notable
thon ultimately ended its censorship program in June overseas exception.
2021 after updating its nodes in compliance with the
Taproot Bitcoin upgrade [159]. Overall, the imperative The majority of mining pools being based in China
of established companies to act in accordance with US was a natural product of the majority of hashrate pro-
regulation is likely to positively frame any future dis- duction residing within Chinese borders. Face-to-face
cussions surrounding mining-related regulations. discussions and relationship development are import-
ant factors when competing to capture such hashrate,
It is also worth noting that several entities already, or which will be further discussed in the “History of
intend to, provide mining pool services with the US as Hardware” section.
Double-Edged Sword of the US Capital Markets
Publicly traded US mining companies are in an ex- For example, consider the December 2020 debt of-
tremely advantageous position when it comes to com- fering by MicroStrategy. After cumulatively investing
peting for the limited supply of hardware, compared to $475 million from their cash reserves into Bitcoin in
smaller-scale miners or startups. Moreover, their track the months leading up to December, MicroStrategy
record of purchases, economies of scale, and access to offered investors $550 million of unsecured convert-
financing enable these entities to access more attractive ible senior debt notes, with the option to purchase an
pricing. For example, a $170 million purchase of 70,000 additional $100 million. The yield on the bonds was
Antminer S19 machines by Marathon announced on 0.75% APY, 50-75 basis points above the Fed Funds
December 28th equated to a purchase price of rough- rate. The offer opened on the 9th of December for 13
ly $25.56 per TH [10]. At the same time, retail miners days and was filled on the 11th of December. Net of
were paying roughly $40.19 on the secondary market fees, MicroStrategy raised $634.9 million [31]. At the
for latest-generation equipment, a 57% premium [5]. end of the five years, the total cost of their capital will
be $24.4 million, paid off in increments over the course
Access to cheap capital is one of the key factors under- of the duration.
pinning this preferential access to mining machines.
US publicly-traded companies have several methods Cheaply raising capital has also extended to the Bitcoin
for financing, with the US capital markets being the mining industry. In January, Marathon raised $250
biggest in the world. Additionally, lower capital costs million by selling equity to several institutional inves-
spurred on by US Federal Reserve interest rate strate- tors, with the deal being brokered by H.C. Wainwright
gies and monetary stimulus decrease capital costs for & Co [32]. The fees incurred to raise such an amount
US based firms. would likely have been a small fraction of the total
capital raised.11
Cheap Financing Increases Valuations
Access to cheap financing is only one of the benefits of ed revenue, such valuations per PH would be unreach-
being publicly listed. These companies are also trading able by private companies. These high valuations can
at valuation multiples that would be outside the realm be strategically used by the management of publicly
of reasonable possibilities for a private company. listed companies to expand their infrastructure.
In January 2021, several mining companies, including For instance, in February 2021, publicly listed Argo
Marathon and Riot Blockchain, surpassed market valu- Blockchain entered into a non-binding Letter of In-
ations of over $1 billion [33, 34]. At the time, Marathon tent (LOI) to issue shares to a New York company to
and Riot Blockchain operated 248 petahash (PH) and purchase 320 acres of land in Texas with access to 800
842 PH respectively, placing their valuations per PH at MW of energy [37]. On the 8th of March, Argo Block-
over $4.03 million and $1.18 million per PH deployed chain finalized the purchase with the intention to build
[9, 35]. 1 PH is roughly 10 Antminer S19 mining ma- a 200 MW facility over the next 12 months [38]. Riot
chines that would currently generate roughly $10,000 Blockchain has also expanded their infrastructure with
per month when no costs are taken into consideration. the acquisition of Texas-based Northern Data, which
If mining conditions remained the same, it would take was partly executed by issuing shares to Northern
over 100 years for the mining machines to generate the Data [39].
valuation that is assigned to their share of the compa-
ny’s hashrate. By April, Marathon and Riot Blockchain Such valuations and the increased negotiating power
increased their installed hashrate to 1,400 and 1,600 that comes with them is certainly a strong incentive for
PH respectively [36]. The market capitalization of both private miners to IPO. Industry professionals anticipate
also increased, bringing their valuation per hashrate to that several mining companies will pursue US IPOs
$3.99 million and $2.99 million respectively [36]. Even over the following year. The public market can also im-
when future expected hashrate for 2021 is taken into pose additional pressure on mining companies. During
account, valuations remain at $538k per PH for Mara- market conditions where Bitcoin price approaches the
thon and $1.26 million per PH for Riot. breakeven levels for some miners, the expenses asso-
ciated with operating a publicly-traded company add
While the market prices in future events, such as future additional pressure.
mining machine deliveries and the resulting anticipat-
Public Versus Private
Private companies do not incur the costly financial re- On the other side, private mining companies will not
porting requirements of their public counterparts. This experience the lofty valuations of public mining com-
places them in a healthier position should market con- panies and will also face a significantly higher cost of
ditions significantly reduce their revenue. The freedom raising capital. Outside of the public markets, the cost
from stringent financial reporting also allows private of raising capital will vary more widely. The company’s
companies to experiment with innovative technologies risk profile and the industry in which it operates will
without broadcasting such developments to the wider significantly impact this cost. For debt financing, the
industry. When Riot Blockchain began exploring an 8 interest rate will rise when a high demand for financing
MW pilot project in Texas with technology infrastruc- meets a limited supply. In the case of the mining indus-
ture companies Lancium and Enigma, this initiative try, there are few commercial lenders and an everlast-
was announced publicly [40]. Should the pilot project ing need for capital due to the imperative of most min-
radically reduce input costs, the development may spur ers to continuously increase their hashing output. This
others to explore such opportunities and diminish Ri- raises the costs of raising capital significantly higher
ot’s advantage. However, a private mining company has than those faced by publicly traded companies.
no obligation to report such initiatives. Some private
mining companies may have a distinct advantage in
how they establish their cost structure.12
Burgeoning Financial Services
The growing demand for capital from US miners is dent from the broader suite of services being offered
evident from several institutions emerging to address by companies like Galaxy Digital and Foundry. Min-
financing and other services in the mining industry. ers can choose from a myriad of companies to access
Galaxy Digital announced the launch of a miner finan- lending and derivatives markets. BitOoda offers several
cial services business line that will offer lending, invest- fully-regulated derivatives products targeted at miners
ment, and risk management services [41]. In September that allow large-scale mining companies to hedge their
2020, Digital Currency Group launched Foundry – a risk exposure. The usage of Bitcoin-collateralized loans
mining-focused subsidiary that will provide services to has also been growing. Data from Credmark estimated
United States miners, including hardware procurement that there was over $25 billion in Bitcoin-backed loans
and financing services. Digital Currency Group com- outstanding at the end of 2020 [44]. Such credit markets
mitted $100 million towards Foundry building out its can serve a useful function for Bitcoin miners, enabling
services [42]. Foundry also secured a partnership with them to meet operational expenses without liquidating
MicroBT to gain priority access to new Whatsminer their current BTC holdings. Several US enterprises
machines for their North American customers [43]. offer such lending services to institutions, including
With this partnership in play, Foundry simultaneously BlockFi, Genesis, and Unchained Capital. BlockFi and
caters to both hardware procurement and financing for Genesis were estimated to have $4.4 billion and $3.8
fleet expansions and upgrades. billion in outstanding Bitcoin-backed loans at the end
of 2020 [44].
Access to financing is only one facet of how the broad-
er capital markets can serve miners and that is evi-
US versus Overseas
However, the US is infamous for its intensive oversight industry. We have observed such markets in a rudi-
on securities, which leave miners with fewer options in mentary form with the launch of hashrate and diffi-
the short-term compared to overseas. Overseas entities culty-based derivatives. Some US entities have listed
like Poolin and Binance have launched token instru- working on the development of widely adopted liquid
ments that are tied to the value of hashrate [45]. US hashrate and derivatives markets among their impera-
companies will refrain from launching products that tives. The financial products and services at the dispos-
likely classify as securities, due to the stringent over- al of US miners can naturally be expected to grow more
sight of the SEC and CFTC. This may give US miners versatile and liquid as the industry grows and more en-
fewer options in the short term. In the long-term, US tities emerge to service miners. Currently, the biggest
companies can be expected to work within the bound- advantage of the US capital markets is the ability for
aries established by regulators to launch innovative fi- publicly traded mining companies to access cheap and
nancial products. abundant capital, capitalize on lofty valuations, and in-
tensely compete for a constricted hardware supply.
The concept of liquid markets surrounding hashrate
and difficulty has been given much attention in the13
The History of Hardware in the United States
Hardware supply is the key constraint facing Bitcoin 70,000 Antminer S19 by Marathon with delivery times
miners globally. With a nearly insatiable demand spread throughout 2021 [10]. Mining machine supply
from efficient miners to increase hashrate, the supply constraints in late 2020 and early 2021 are further ex-
of new mining machines is insufficient to meet mar- acerbated by global semiconductor shortages. Sectors
ket demand. Demand-supply imbalances exacerbate like the US auto industry have had cases of halting pro-
during spans of lucrative mining conditions. In the duction and furloughing workers due to an ability to
competition to secure supply, mining facilities com- secure semiconductors in a market where demand far
mit to purchases with lengthy future delivery dates as outweighs supply [46].
was highlighted by the December 2020 purchase of
Hardware Market Characteristics
Miners that can’t secure hardware from manufacturers
are forced to pay premiums in the secondary market or Given that Bitcoin price directly impacts the profitabil-
purchase through brokers that add a significant markup ity of mining, the price movement of latest-generation
to equipment. Brokers typically add markups of 6-15% mining machines is positively correlated with Bitcoin
for new equipment and 15-25% for used equipment. price. From April 6th 2020 until the 22nd of February
The secondary market also incorporates a significant 2021, weekly data for latest-generation mining ma-
premium compared to purchasing directly from manu- chines with an efficiency of under 38 J/TH recorded a
facturers, as highlighted by the 57% difference between correlation coefficient of 0.968 with Bitcoin price, al-
what Marathon paid for Antminer S19 machines and most perfect correlation [47].
the price of sale on the secondary market [5, 10].14
Before the Antminer S19 and Whatsminer M30S min- et, and a high failure rate in the S17 series of hardware.
ing machines became the latest generation, Antminer Data suggests that more bidirectional Bitcoin price
S17 machines were the most efficient on the market. movements, or more weeks where Bitcoin price record-
Released in April 2019, the initial S17 model touted an ed declines, may be a contributing factor to the lower
energy efficiency of 45 J/TH. S17 machines were posi- correlation strength. In the first dataset (April 2020 to
tioned as the latest-generation until the release of the February 2021), 32 of the 47 weeks analyzed, 68%, re-
S19 series in April 2020. While these machines were corded Bitcoin price increases whereas, in the second
the latest-generation, the correlation coefficient be- data set (April 2019 to March 2020), only 25 of the
tween weekly Bitcoin price data and mining machines 52 weeks analyzed, 48%, recorded price increases [47].
in the bracket of 38-60 J/TH between April 1st 2019 It makes intuitive sense that Bitcoin price conditions
to March 30th 2020 was 0.403, moderately positively are a significant contributing factor to the correlation
correlated but far less so than the previous dataset [47]. strength between price and machine price. As the price
of bitcoin rises, demand for mining will naturally in-
The lower correlation strength could be attributable crease. However, given the lack of supply in the hard-
to several factors like more bidirectional Bitcoin price ware market, a lower Bitcoin price might not necessar-
movements in the time analyzed, the inclusion of some ily reduce demand.
mid-gen machines in the 38-60 J/TH efficiency brack-
This reasoning is further corroborated by the correla- ing machine equipment in the bracket of 60-100 J/TH,
tion of Bitcoin price data with old-generation equip- S9 series hardware, was 0.972 from April 6th 2020 to
ment. The price correlation of Bitcoin price with min- February 22nd 2021.15 In contrast, the correlation dropped to 0.273 when the those with the most competitive power prices will be data was analyzed between April 1st 2019 and March able to profitably operate such equipment. However, 30th 2019. Correlation may also decline as equipment the stark contrast in correlation figures suggests that advances in generation, as the market size interested in Bitcoin price conditions are the prevailing factor im- such equipment becomes progressively smaller, as only pacting the correlation.
16 Fluctuation in hardware prices presents a challenge to ware from vendors. Manufacturers typically keep their institutional buyers. In times of volatile Bitcoin market prices stable for at least two weeks which makes the conditions, hardware prices will vary day-to-day. This procurement process smoother compared to the sec- adds an extra layer of complexity for institutions that ondary market where prices fluctuate daily. Moreover, may have strict risk and compliance measures. Given institutional and large-scale miners can leverage long- that brokers add a significant markup, they are more term relationships with vendors to secure preferential suitable for smaller-scale and retail miners, as opposed pricing compared to what a smaller-scale miner could to industrial miners who aggressively minimize input expect to negotiate. costs. Institutional miners will typically secure hard- Historical Hardware Procurement Difficulties Facing US Miners Until recently, the hardware procurement process ders only being partially fulfilled and pre-used mining faced by United States miners was marred with friction machines being delivered. Manufacturers mining with and complications. Miners were forced to fully prepay hardware before delivering it to customers is an un- for mining machines several months in advance. As confirmed but widely believed facet of the early-stage manufacturers were based in China, this meant wiring Bitcoin ASIC manufacturing industry. With two of the payment to an overseas entity. United States miners five major hardware manufacturers after publicly list- also had little control over the delivery process. Equip- ing, and the market leader Bitmain working towards ment may be delivered to a state that was distant from an IPO, such purported practices are quickly becoming a miner’s facility and further delivery would need to be anachronistic as professionalism improves among the organized by the miner. There are several reports of or- major manufacturers. Miners in the US have historically been at a distinct of new generations of mining machines, especially in disadvantage to Chinese miners. Chinese miners could the early generations, were particularly profitable, as develop close relationships with their domestic manu- the mining machines were deployed at a difficulty level facturers and position themselves as a priority to receive that has yet to register more powerful mining machines new mining machines releases. The initial deployment coming online.
17
US-based miners have also faced historicallyunfavor- networks. Their presence and personal connections
able dynamics on the hardware front. Significant geo- with domestic manufacturers have historically secured
graphical distance from the hardware manufacturers preferential treatment for Chinese miners. Overseas
means that United States miners can expect to receive miners were also at a disadvantage when it came to
equipment several months after their Chinese coun- industry developments and hardware repair. The Bit-
terparts, with difficulty levels after adjusting to reflect coin ASIC manufacturing industry wholly resided in
more powerful hardware coming online. United States China and there was a significant separation between
miners were also at a disadvantage due to the dissimi- Chinese miners and miners operating elsewhere. Re-
lar business practices in China. Personal relationships lations between China and the United States have also
and networks play an important role in how business is been turbulent on a political level. During the Trump
conducted in China. Guanxi (关系) is a Chinese term that administration, the government imposed a 2.6% duty
expresses the importance of developing such personal and 25% tariff on hardware imported from China [48].
Hardware Manufacturer Institutionalization
This has slowly changed and the disadvantage faced by purchase orders, reducing the risk faced by an institu-
United States miners has been dissipating. When mass- tion that embarks on securing such an order. This is far
scale ASIC manufacturers initially emerged in 2013, more suitable for large institutions that may have strict
the market they addressed was vastly different from the risk and compliance measures. In previous years, the
one they face today. The annualized coinbase rewards uncertainty relating to whether a manufacturer could
earned by miners grew from under $20 million at the successfully deliver an order was far greater. Manufac-
start of 2013 to a market worth of over $10 billion in turers have also placed a greater emphasis on servic-
2021 [49]. The increasing value inherent in the industry ing overseas clients. Both Bitmain and MicroBT have
is accompanied by an increasing institutionalization of established facilities in Southeast Asia to allow United
ASIC manufacturers. Two ASIC manufacturers – Ca- States miners to circumvent the 25% tariff on equip-
naan and Ebang – have carried out IPOs in the United ment imported directly from China [43]. Partnerships
States. The market leaders Bitmain and MicroBT are are being formed with overseas mining companies. For
both anticipated to follow with their respective IPOs. instance, Core Scientific operates an in-warranty re-
The reality of being a publicly traded company servic- pair center for Bitmain’s Antminer mining machines.
ing a multi-billion dollar annual market starkly con- Foundry has secured a partnership with MicroBT to
trasts the conditions facing a 2013 Chinese startup that gain priority access to equipment for the United States
is venturing into a high-risk market with immensely institutional miners that they work with [43].
uncertain prospects. Being publicly-traded demands
much higher levels of professionalism from listed en- As it stands, hardware is the defining bottleneck for
terprises. Instances of uncertain hardware deliveries growth in the US mining industry. Increasing profes-
and used equipment being delivered will be replaced sionalization is one factor that has unfolded in favor
by ironclad purchase agreements and ancillary services of the US mining industry. However, there are several
to maximize quality. more unfolding that could radically change the scale
of Bitcoin mining in the US. In Chapter 2, we consid-
It is already evident that the environment facing over- er how the hardware industry may evolve moving for-
seas miners is vastly different from the one of previous ward and its connotations for US miners.
times. Manufacturers are frequently carrying out large18
The Complexity and Opportunity in the US Energy Market
The United States is an extremely energy-rich coun- ket in the US is extremely complex, with its structure
try with a production of roughly 101 quadrillion BTU, and regulations varying from state-to-state, and most
ranking the country as the largest producer of energy operators servicing multiple states. Sourcing electricity
after China [50]. Harry Sudock has noted that “power can also be a challenge in some cases, but circumstanc-
availability” is one of the main factors making the US es will widely vary depending on the region.
an attractive region for miners [4]. The electricity mar-
Sourcing Energy in the US Electricity Market
Consumers in the US market can either source their en- serve consumers [51]. These markets exist primari-
ergy behind-the-meter, directly from a power provider, ly in the Southeast, Southwest, and the Northwest of
or in front of the meter, through a deregulated com- the US. Utilities hold exclusive territory rights in these
petitive wholesale market or a regulated utility compa- areas. Large-scale consumers can negotiate directly
ny. On a state level, the reality facing miners sourcing with the utility companies to secure a power price. It
energy will vary widely based on the specifics of each is also possible to secure behind-the-meter energy in
state. Roughly one-third of the country’s electrici- these markets. These regions are mapped in white on
ty demand is met via traditional regulated electricity the below map.
markets where vertically integrated utility companies
(Source: ferc.gov , 51)
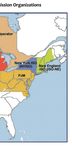
Roughly 2/3rds of electricity demand is located in a to ensure that demand matches supply and to source
deregulated jurisdiction which is primarily serviced by the lowest cost energy for the grid. The ISO’s are la-
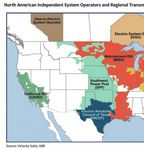
one of the nine Independent System Operators (ISO). belled on the above map. The Electric Reliability Coun-
These regions operate through competitive market cil of Texas (ERCOT) is a particularly pertinent ISO
mechanisms with supply-side power sources bidding for miners.
to be included in the market. The role of the ISO is19
Texas offers extremely attractive conditions for both nite transmission infrastructure. West Texas is a hub
miners who source behind-the-meter and those that for wind power production but has limited local de-
participate in the ERCOT market. Bitcoin miners in mand. Electricity prices can turn negative in the region
the ERCOT market can significantly reduce their effec- to incentivize wind producers to disconnect from the
tive power price by participating in demand-response grid. Wind producers will often persist to produce until
programs. ERCOT is particularly prone to volatile rates turn to a given negative level as they receive sub-
power prices which fosters extremely lucrative condi- sidies from the federal and state governments for their
tions for participants of demand-response programs. renewable energy production.
West Texas is a particularly attractive region due to fi-
ERCOT Cost Breakdown and Demand-Response Programs
Base energy prices in the ERCOT market are extreme- ator, ERCOT, the right to curtail the LR’s energy con-
ly competitive. Over the past five years, the wholesale sumption to address large unforeseen frequency drops
base energy cost averaged roughly $0.03 per kWh [52]. in the grid that require additional energy or load inter-
Uplift charges are limited and are roughly $0.002 per ruption to restore the frequency back to normal levels.
kWh. ERCOT is the only US ISO with no capacity pay- LRs are compensated for participating in this program.
ments and renewable energy credits are nearly non-ex- The RRS price is typically highest when the opportu-
istent, bringing the costs associated with these close to nity cost for generation is at its highest. CLRs can also
zero. The distribution of energy can be split into two participate in additional demand-response programs
parts – transmission and distribution. The transmission such as Reg-Up/Reg-Down and Non-Spin.
consists of high-voltage transmission lines that trans- The RRS AS program is oversubscribed and LRs only
fer energy from generators to consumption hub load receive prorated compensation on their bids. In 2020,
zones like cities. The cost associated with the transmis- approximately 7,000 MWs competed for 1500 MWs of
sion is roughly $0.006 per kWh. After the high-volt- RRS [52]. The rewards were distributed proportionally
age transmission lines, the energy is carried through and LR participants received roughly 37 cents on every
a transformer where it is transferred to lower-voltage dollar for their RRS offers [52]. A more attractive op-
distribution lines that deliver it to the end consumer. tion for consumers is participating in the demand re-
sponse programs that are available to CLRs. However,
Distribution charges can be avoided by building a the requirements for becoming a CLR are higher and
private substation that connects to the transmission require entities to demonstrate technical characteris-
lines. Transmission line charges can also be avoided by tics similar to a power generator like receiving baseline
curtailing energy during what are called “coincident directives from ERCOT and being able to ramp up and
peaks” of demand during the summer months of June ramp down energy consumption. CLRs must be able
through September. These can be easily forecasted by to instantaneously respond to frequency deviations on
consumers. However, the ERCOT market is particular- the ERCOT grid. Those that participate in the CLR pro-
ly attractive to miners as they can significantly reduce gram do not compete against those in the LR market.
their effective power price by participating in the mar- They compete against power generators who face real
ket’s other demand-response programs. opportunity costs when offering to sell energy versus
participating in demand-response programs. As long
In ERCOT, there are two types of demand-response as the CLR has an offer price that is less than what was
program participants, known as Load Resources (LR). offered across the power generation, they will receive a
A Controllable Load Resource (CLR) is capable of full award and receive the full reward amount. By par-
controllably reducing or increasing consumption in ticipating in the CLR demand-response programs, the
response to signals by ERCOT. A non-Controllable Re- potential to reduce your effective electricity price is far
source (non-CLR) gives the right to ERCOT to curtail greater compared to other US ISO’s. CLR participants
their energy consumption under certain circumstanc- are also agnostic to location as participation is grid-
es. In the ERCOT market, LRs can participate in the wide and the rewards for participating in the CLR pro-
Regulating Reserve Service (RRS) AS product market gram are priced according to the most volatile power
where Load Resources agree to give the system oper- prices across the ERCOT grid. Lancium is a technolo-20
gy infrastructure company in Texas that has a patent- tricity from a more distributed energy mix. Notably,
ed software – “Smart Response” – designed to enable New York is the third-largest producer of hydropower
Bitcoin miners to be eligible for participation in CLR in the US, which is particularly well-suited to cater-
demand-response programs. In August 2020, Lancium ing to unexpected demand increases [56]. Moreover,
entered into a lawsuit with Texas company Layer1 for an analysis by Joshua D. Rhodes shows that ERCOT
patent infringement [53]. The litigation was settled in has been sourcing an increased share of its energy
March 2021 with Layer1 resolving to licence the “Smart from renewable sources. Coal is accounting for a lower
Response” software [54]. portion of fuel mixes, making the role of demand-re-
sponse programs like the CLR more important as the
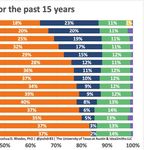
For the past two years, providing such demand-response redundancy that was once in place from coal plants is
services through CLR demand-response programs has being diminished. It took approximately 15 years for
enabled consumers to reduce their base power price by the percent of total annual energy generated by wind
roughly 50%. For comparison, the demand response in ERCOT to progress from roughly 2% in 2006 to 23%
programs in the New York ISO (NYISO) enables con- in 2020. With solar representing 2% of generation in
sumers to reduce their base power price by roughly 2020, it is not improbable to think solar will follow a
15-20%. The energy mix of the state plays a key role similar path to wind over the next 15 years. If this ma-
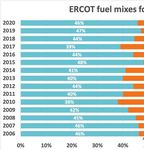
in determining the lucrativeness of demand-response terializes, wind and solar would represent roughly half
programs. Roughly half of Texas energy production of the energy generated in ERCOT with coal continu-
is generated by burning natural gas, and power plants ing to lose its production share. In this scenario, having
keep little reserves on-site making demand-response CLR entities available to ERCOT for primary frequen-
programs more important during unexpected shifts in cy response and demand response programs overall
demand [55]. In contrast, the NYISO generates elec- will become more important for grid stability.
(Source: Twitter.com, 57)You can also read