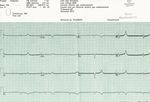
Jennifer Carlquist PA-C, ER CAQ SVMH, Central Coast Cardiology, CHOMP ER, Watsonville ER - GAPA
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Objectives Review normal cardiac conduction Rhythm review How to assess heart rate 10 step program to assess an EKG Normal EKG review Where’s the STEMI? Trouble Shooting
You have to know what normal is to know what abnormal is. Introducing…. NSR. When the president is in charge.
Who runs the heart? President VP Secretary Speaker of House The heart is like a committee – every member has a vote and voice
When everyone tries to overthrow the government
When the president goes on vacation…
Patient dizzy. PMD put her on Metoprolol 100
mg for HTN.CHADS2VASC: 3. Treatment?
Sinus Tachycardia
Rate: >100 – 160 BPM
Regularity: Regular
P wave: Present, PR interval constant
__________________ and _________ can cause sinus tachycardia.SVT
These patients will most likely have a ___________ blood
pressure.36 y/o military wife with four kids
Atrial Fibrillation
Rate: Variable, ventricular response can be fast or slow.
Regularity: Irregularly irregular
P wave: None; chaotic atrial activity
Patients lose their ___________ in atrial fibrillation.10 Step Program 1.What is my general impression? 2.Is there anything that sticks out? 3.What is the rate? 4.What are the intervals? 5.What is the rhythm? 6.What is the axis? 7.Is there any hypertrophy? 8.Is there any ischemia or infarction? 9.What is the differential diagnosis of the abnormality? 10. How can I put it all together with the patient?
These numbers……MATTER PR Interval - .12 - .20 (120 ms – 200 ms) QRS Complex - below .12 (120 ms) QT Interval – below 460 ms A normal QRS should be no longer than ____ boxes
Is this EKG normal? Rate: 60 – 100 BPM PR: 120-200 MS QRS: under 120 MS QTc: 460 MS Axis: 0 - 90
It is as easy as this… P – P wave? PR interval? Q – QRS – wide? QT interval? Q Wave? R – Rate? Rhythm? RR interval? S – ST elevation? T – T waves (shape, size, position)
Nitty Gritty Basics
Six second method
Example EKG Lets look at the intervals
Problem P waves
T Wave Corresponds to the rapid ventricular repolarization Normally rounded and positive R on T phenomenon
T Wave Mugshots
What is happening here?
LAD occlusion
Q Waves Non Pathologic Q waves Q waves of less than 1/3 R Pathologic Q waves 1/3 height of R wave
Pathologic Q waves
What part of the heart can we not see here?
Which ones are “contiguous”?
AVR VI
Lead I v4
II AVL V2 v5
III AVF V3 V6“Reciprocal changes”
Where’s the STEMI
MIIs this a STEMI?
How I approach an EKG • Fast/ Slow • Arrhythmia • MI Intervene Intervene Intervene
Second Tier Triage
Subtle MI
Stemi
Mimic
C/C basedPalpitations
tree
Getting to the
root of the
cause
AFIB/Flutter
PVC’s
SVT WPW Sick sinus VTPriority Chief Complaints Palpitations – WPW, SVT, AF. VT Chest pain – MI, S1, q3, T3 Dyspnea – MI, s1, q3, t3, R axis, LVH Dizzy light headed – Arrhythmia, QT, WPW Weakness – EVERYTHING Dialysis – peaked T, slow rate
17 year old with Palpitations WAVE PR interval (
Lets try our six second method…
Weakness in a 70 year old
Really, computer?
Is the hr correct?
Somatic Tremors
“Toothbrush Tachycardia”
Baseline Sway Figure 4-4: Baseline Sway
60-Cycle Interference Figure 4-5: 60-Cycle Interference
Take Home Points The president should always run the heart Don’t trust the EKG interpretation PQRST The EKG family should always be holding hands Memorize your intervals Know the big bad wolves
Jcarlquist.com
References
12-Lead ECG: The Art Of Interpretation – Tomas Garcia
Friberg L, Rosenqvist M, Lip GY. Evaluation of risk stratification schemes for ischaemic stroke
and bleeding in 182 678 patients with atrial fibrillation: the Swedish Atrial Fibrillation cohort
study. Eur Heart J 2012; 33:1500.
Electrophysiology: Ventricular tachycardia: diagnosis of broad QRS complex tachycardia.
AU Wellens HJ
SO Heart. 2001;86(5):579
Miller JM, Hsia HH, Rothman SA, et al. Ventricular tachycardia versus supraventricular
tachycardia with aberration: electrocardiographic distinctions. In: Cardiac
Electrophysiology From Cell to Bedside, Zipes DP, Jalife Jose (Eds), W.B. Saunders,
Philadelphia 2000. p.696.
Akhtar M, Shenasa M, Jazayeri M, et al. Wide QRS complex tachycardia. Reappraisal of a
common clinical problem. Ann Intern Med 1988; 109:905.You can also read