Understanding Martian sulfates - Washington University in St. Louis
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Understanding
Martian sulfates
DR ALIAN WANG
In the quest to discover more about our neighbouring planet, Dr Alian Wang
and her team are carrying out experimental investigations on the fundamental
properties of hydrous sulfates found on Mars, using laser Raman spectroscopy
of inorganic (mineral) and organic (biomarker) rich regolith and phyllosilicate-bearing
species during robotic surface explorations rocks, I have used data from all scientific
on Mars. Compared with other spectroscopic instrument payloads, as well as support
techniques, LRS provides information on from mechanical engineers and atmospheric
molecules, for example chemical bonding and scientists. Furthermore, in order to
crystal structure. Moreover, LRS peaks are understand our Mars observations on sulfate
much sharper and almost free of overtones dehydration, I run laboratory experiments
and combination modes, thus giving more on hydrous sulfates, liaise with theoretical
distinct fingerprint spectra with a very low modelling experts, and travel to terrestrial
degree of peak-overlaps for mixtures (such field sites like the Tibetan Plateau and the
as soils and rocks on the surface of Mars). Atacama Desert to see analogous subsurface
LRS is extremely sensitive to carbon, and salty layers.
can distinguish the structural variations in
carbonaceous materials, thus it can be useful Do you have any current or future
in the search for traces of life. research plans?
LRS is the major phase identification tool that My team is starting systematic experimental
my team used in the experimental study of studies on the stability fields and reaction
fundamental properties of hydrous sulfates. rates of hydrous Al-sulfates and chloride
Could you begin by outlining the main Our studies demonstrated that LRS can provide hydrates. Al-sulfates should be formed from
objectives of your research? conclusive characterisation of sulfates with extensive weathering processes, thus they
various hydration degrees and solid-solution are less likely to exist in large quantities and
Hydrous sulfates are one of the two major sulfates with different cations. be widespread on Mars. However, Al-sulfates
types of secondary minerals (the other type were actually observed by orbital remote
is phyllosilicates) that have been found in What are the difficulties associated with sensing in localised areas, so are worth
large quantities and widely spread on the LRS? Are there specific problems relating more detailed study. More importantly, we
surface of Mars. The hydration degree of these to its use in space? How do you overcome need to compare the reaction rates among
sulfates on the martian surface is influenced these issues? the common Mg, Fe, Ca, and Al-sulfates
by environmental conditions, which are through experiments.
determined by the diurnal and seasonal Raman scattering is intrinsically a weak
cycles, and in the long term, by the cycles of process. We need to collect as many Raman In addition, we propose that a subsurface layer
Mars’ obliquity. photons as possible from a sample, while, at of chloride hydrates could be the potential
the same time, reduce the photon loss in the source for recurring slope lineae (RSL) which
The current degrees of hydration of Mg, Fe, Ca optical train and prevent the interference from have been observed on many equator-facing
and Al-sulfates at the surface and subsurface of other light sources. Having good optical design slopes during warm seasons on Mars. The
Mars can shed light on the hydrologic evolution is the key, as well as first-class mechanical, assesment of their stability fields under
of the planet, and provide information about thermal and electronic subsystems to ensure Mars’ subsurface conditions and the rate of
its current water reservoirs. Both aspects relate a robust flight system. Our engineering team deliquescence as a function of temperature
to the potential formation and preservation of at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) has will help improve understanding of RSL
Martian life (if that ever happened). Laboratory been working on these issues and have found phenomena, and can further address questions
experimental studies on the stability fields and good solutions. about Mars’ hydrologic history and current
reaction rates of hydrous sulfates under Mars- water reservoirs.
relevant conditions can be used to explain How important are collaboration and
phenomena observed during past and current embracing an interdisciplinary approach to Another even more important plan is to
exploration missions on the planet. the Mars Rover project? propose the laser Raman system that we
(Washington University in St Louis and JPL)
In what ways can laser Raman spectroscopy I benefited greatly from interdisciplinary have been developing as a science payload
help to deepen our understanding of Mars? collaborations during the Mars Exploration for the NASA Mars 2020 Mission. Having this
Rover Mission. Over the past nine years, I Raman system as a fine-scale mineralogy tool
Laser Raman spectroscopy (LRS) has been have worked mainly in a mineralogy and will allow us to characterise – directly and in
proposed as a powerful new technique for geochemistry ‘theme group’; while for situ – the hydrous sulfates on Mars’ surface and
definitive identification and characterisation my investigations on subsurface sulfate- within the subsurface.
WWW.RESEARCHMEDIA.EU 39DR ALIAN WANG
Mission to Mars
Researchers at Washington University in St Louis are investigating the fundamental properties of subsurface
materials found on Mars to shed light on its evolution and their significance to other planetary bodies
AS ON EARTH, SULFATES and hydrated LASER RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY
sulfate minerals have been found in
abundant quantities on the surface of One research group studying the fundamental
Mars; identified as a result of spectroscopic properties of hydrous sulfates relevant to
observations from orbital remote sensing Mars is based at Washington University in
as well as landed exploration missions by St Louis, USA. Led by Dr Alian Wang, the
rovers. This discovery implies that there group is investigating stability fields, phase
is substantial sulfur cycling taking place transition pathways and reaction rates of
among gases, liquids and solids on the hydrous sulfates likely to be found on the
planet, and that Martian sulfates may have planet. The researchers current project is one
played a critical role in the weathering of of two that has been funded by the NASA
surface and subsurface materials, circulation Mars Fundamental Research Program. Over
of metals, circulation and storage of water eight years, Wang’s team has conducted two
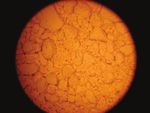
and hydroxyl, and the hydrologic processes sets of systematic experimental investigations Wang’s team synthesised a set of OH-bearing ferric sulfates
that took place over the course of Mars’ in Earth atmospheric pressure and under Mars to study their thermodynamic and kinetic properties.
long history. As many of these sulfates have relevant atmospheric pressure into Mg and
been found in layers that have thicknesses ferric sulfates, and it is currently embarking on spectroscopic tools, LRS gives very dinstinct
rarely seen in terrestrial deposits, scientists a study of Al-sulfates. fingerprint spectra, which permit detection of
are keen to understand the environmental minor changes in hydration degree and the co-
conditions that have enabled such large The group is working with information from existence of multiple sulfates.
amounts of layered sulfate deposition to three rovers (Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity)
take place. and three orbiters (Mars Express, ODY and
SUBSURFACE MINERAL WATER RESERVOIR
MRO) on Mars. In the laboratory, they are using
However, the findings from past and laser Raman spectroscopy (LRS) as a major By exploring their general hypothesis – that
current missions to Mars revealed very little tool to monitor the phase transitions. LRS is there is likely to be a subsurface mineral
information about the degree of hydration a spectroscopic technique used to observe water reservoir on Mars – the group has
of martian minerals; information that is vibrational, rotational and other low-frequency successfully revealed stability fields and rates
essential to enable scientists to interpret modes in a molecular system. Modern Raman of dehydration and rehydration for a range
the hydrologic history of the planet. spectroscopy uses a laser to stimulate Raman of hydrous sulfates. Specifically, it conducted
Consequently, laboratory experiments scattering from a sample, collect the Raman experiments at three different temperature
carried out on Mars-relevant sulfates under photons and analyse their wavelengths. The scenarios with Mars-relevant atmospheric
Mars-relevant conditions can enhance energy difference between the excitation laser pressure and partial water pressure to extract
understanding about the degree of hydration and the photons is called the ‘Raman shift’ the activation energy and extrapolate the
of different ubiquitous sulfates at various which is dependent entirely upon the structure half-life of dehydration of sulfates on the
seasons and locations and during the change and composition of the molecule that is subsurface of Mars. “At low temperature, the
of Mars’ obliquity periods. emitting the photons. Compared with other sulfates with a high degree of hydration have
enlarged stability fields toward low relative
humidity,” Wang elucidates. “They are capable
of maintaining high relative humidity in a
closed environment and an aqueous film at
their grain surfaces. More importantly, their
dehydration processes are much slower than
water-ice sublimation.”
Using the experimentally extracted activation
energy and half-life, they found that
subsurface hydrous Mg-sulfates which formed
during past high obliquity periods have a
high probability of maintaining mid- to high-
degrees of hydration, possibly until the present
Wang’s team joined a field expedition to saline lakes and Wang led a team of US scientists on a field expedition to epoch. Among the Mg, Fe, Ca and Al-sulfates
playas at Atacama desert, to test instruments developed the saline lakes and playas of the Tibetan plateau to study explored, they found that Mg varieties have the
for future planetary missions. hydrous sulfates at the surface and subsurface. lowest thermal stability, suggesting that the
40 INTERNATIONAL INNOVATIONINTELLIGENCE
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF
SULFATES RELEVANT TO MARS: STABILITY
FIELDS, PHASE TRANSITION PATHWAYS
AND REACTION RATES
OBJECTIVES
To understand the past and current status of
Subsurface Mineralogical Water Reservoirs on
Wang’s team is making measurements using laser Wang’s team uses a new facility, laser Raman Mars through studying the changes of hydration
induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and laser Spectroscopic imaging, to study extraterrestrial materials. degrees of sulfates affected by atmospheric
Raman spectroscopy (LRS) of the samples in a Mars and subsurface environmental conditions.
environmental chamber. Shedding light on their evolution as influenced
by the martian obliquity cycle, this will improve
remaining sulfates on Mars must dehydrate steep slopes and appears to grow incrementally understanding of Mars’ hydrologic history.
even slower. during warm seasons and reduce during cold KEY COLLABORATORS
seasons, possibly pointing to evidence of past
These results are consistent with an excavation liquid water flow. Scott Rudolph Professor of Earth and Planetary
Sciences Bradley L Jolliff; James S McDonnell
made by the Spirit rover at Gusev Crater on Mars,
Distinguished University Professor Raymond
where evidence of dehydration of subsurface Fe This premise is supported by the widespread E Arvidson, Washington University in St Louis,
sulfates was found after their exposure at the existence of chlorine on Mars, putative USA • Research Geologist I-Ming Chou, U.S.
surface. Furthermore, they are consistent with chloride deposits in the southern hemisphere Geological Survey • Dr William C Feldman,
the findings of highly hydrated sulfate (epsomite) of the planet and especially by the properties Planetary Science Institute, New Mexico, USA
and chloride (carnallite) in the subsurface of of chloride hydrates revealed in previous • Staff Scientist Michael T Mellon, Southwest
a hyper-arid Mars analogue site, the Da Lang studies of saline fluid inclusions within Research Institute, Texas, USA • Academician
Tan saline playa on the Tibetan Plateau. “Our terrestrial rocks. Wang’s group is just beginning MianPing Zheng, PhD, Chinese Academy of
study supports our hypothesis that subsurface a systematic experimental study on chloride Geological Sciences, China
hydrated sulfates hosting large amounts of hydrates but their preliminary results show PARTNER
water are major contributors to high water- that the temperature dependence of their
equivalent-hydrogen (WEH) values observed at stability fields and the extremely fast rates of NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory
two equatorial regions on Mars,” Wang adds. deliquence processes when required conditions FUNDING
On Earth, this type of subsurface environment are met support the hypothesis.
NASA, Mars Fundamental Research Program
is life-friendly, as demonstrated by the discovery – grant nos. NNX07AQ34G, NNX10AM89G •
of halophiles in salt-rich subsurfaces in the NASA, Science Team support for MER mission
BROAD AND DEEP SIGNIFICANCE
Atacama Desert and Tibetan Plateau. and MoO support for Wang as Co-PI in ESA
The rovers and orbiters currently working at ExoMars rover mission • NASA’s Planetary
Mars’ surface and in orbits are generating Instrument Definition and Development
RECURRING SLOPE LINEAE Program (PIDDP), Mars Instrument
exciting new information every day and
A related hypothesis proposed by the will – in the near future – study thick sulfate Development Project (MIDP), Astrobiology
group is that chloride hydrates may exist deposits found at depth. Two further orbiter Science and Technology for Exploring Planets
in some areas within the subsurface of the missions to the planet (Maven 2013, Trace (ASTEP) and Maturation of Instruments for Solar
System Exploration (MatISSE) programmes •
southern hemisphere on Mars and that the Gas Orbiter 2016) and three more landed McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences at
deliquescence of these chloride hydrates at missions (InSight Mars 2016 Lander, ExoMars Washington University in St Louis
elevated temperatures may produce large 2018 and Mars 2020 Mission) are currently
quantities of brine that cause an event known under development. As a result, more CONTACT
as recurring slope lineae (RSL). Repeatedly information from the planet will be obtained, Dr Alian Wang
observed on Mars, this phenomenon occurs on enabling a deeper understanding of Mars as a Research Professor and Principal Investigator
dynamic system; from atmosphere, to surface
and subsurface material to interior structure. Earth and Planetary Sciences
McDonnell Center for Space Sciences
Washington University in St Louis
The outcomes of Wang’s research have broad Office – Rudolph Hall, Room 338
and deep scientific significance as sulfates Campus Box 1169, 1 Brookings Drive
and hydrated sulfate minerals are anticipated Saint Louis, Missouri 63130-4899, USA
to exist not only on Mars but also on many
other planetary bodies, for example Europa, T +1 314 935 5671
E alianw@levee.wustl.edu
an icy-satellite of Jupiter. “Getting unaltered
records from other planets like Mars will help
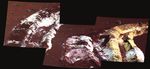
Subsurface salty soils excavated by the Spirit Rover ALIAN WANG is a Research Professor at
at ‘Tyrone’ site near Home Plate at Gusev Crater. The
us to understand the processes that our own Washington University in St Louis and a
yellowish salty soil enriched with ferric sulfates was dug Earth has experienced during its early age. renowned laser Raman spectroscopist,
out from a deeper depth by the non-function right-front Understanding the current status of other specialising in its applications for planetary
wheel of the Spirit rover. A colour change was observed planets will help us to see the potential future surface exploration and planetary fundamental
after ~ 200 sols. of our own home,” Wang enthuses. science investigations. She is the Principal
Investigator of Mars Microbeam Raman
Spectrometer (MMRS) supported by NASA
PIDDP, MIDP, ASTEP and MatISSE programmes.
WWW.RESEARCHMEDIA.EU 41You can also read