Topiramate Induced Bilateral Angle-closure Glaucoma
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Topiramate Induced Glaucoma • Sorkhabi et al Iranian Journal of Ophthalmology • Volume 20 • Number 3 • 2008
Topiramate Induced Bilateral Angle-closure Glaucoma
Rana Sorkhabi, MD1 • Nazli Taheri, MD2
Abstract
Downloaded from irjo.org at 17:32 +0430 on Monday April 8th 2019
Purpose: To describe a case of acute angle-closure glaucoma associated with oral topiramate
(Topamax, Aria Daroo) therapy
Case report: Two weeks after initiation of oral topiramate therapy for epilepsy, a 35-year-old woman
presented with blurred vision and headache. Intraocular pressure in both eyes was significantly
elevated and her visual acuity was 20/30 Ocular Uterque (OU). Bilateral conjunctival chemosis,
shallow anterior chamber and mild corneal edema were observed. Topiramate therapy was
discontinued. Topical therapy was initiated in both eyes with betamethasone, atropine and timolol
Results: Symptoms and signs including vision accuracy, refraction and intraocular pressure
resolved over the next 2 weeks.
Conclusion: Topiramate therapy may be associated with ciliochoroidal effusion resulting in angle-
closure glaucoma; therefore, patients on such therapy should be carefully monitored.
Keywords: Topiramate, Angle-closure Glaucoma, Ciliochoroidal Effusion
Iranian Journal of Ophthalmology 2008; 20(3):49-52
Introduction
Topiramate (Topamax, Aria Daroo) is an oral medical sciences for a three day history of
sulfamate medication used mainly for seizure bilateral frontal headache and blurred vision.
treatment and is also used in the management Her medical history was notable for epilepsy.
of migraine, depression and neuropathic Her ocular medical history was unremarkable.
pain.1 Off-label, it has gained popularity as a She had never worn glasses, and she did not
weight reducing agent and a treatment for recall any cases of ocular diseases within her
bipolar disorder.2 family. Her medications included oral
Topiramate may cause idiosyncratic topiramate at 100 mg twice daily, which she
ciliochoroidal detachments and ciliary body had started 2 weeks before she came. At the
edema leading to anterior displacement of the time of presentation, her visual acuity was 20/30
lens-iris diaphragm, lens thickening, and acute Ocular Uterque (OU). Manifest refraction
angle-closure glaucoma.3 revealed -0.75 dioptres myopia in both eyes.
Herein, we present a case of acute angle- In both eyes, slit-lamp examination revealed
closure glaucoma, developed two weeks after conjunctival chemosis and injection, mild
starting oral topiramate therapy. corneal edema, and markedly shallow anterior
chamber (Figure 1). Intraocular pressure (IOP)
Case report was measured as 29 mm Hg OD and 31 mm
A 35-year-old woman was examined at the Hg OS. Gonioscopy revealed closed angles
ophthalmology clinic of Tabriz University of (Figure 2).
1. Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, Nikookari Eye Hospital, Tabriz Correspondence to:
University of Medical Sciences Rana Sorkhabi, MD
Nikookari Eye Hospital, Tabriz
2. Resident in Ophthalmology, Nikookari Eye Hospital, Tabriz University of Tel:+98 411 6551332
Medical Sciences Email: sorkhabi-r@yahoo.com
Received: January 23, 2008
Accepted: March 15, 2008
49Topiramate Induced Glaucoma • Sorkhabi et al Iranian Journal of Ophthalmology • Volume 20 • Number 3 • 2008
biomicroscopy demonstrated a closed angle
with a forward shift of the lens, and swollen
ciliary processes (Figure 3).
A-scan and B-scan ultrasonography revealed
anterior chamber depth of 1.1, 1 mm in right
and left eye respectively and 360°
ciliochoroidal effusion in both eyes (Figure 4-
A).
Downloaded from irjo.org at 17:32 +0430 on Monday April 8th 2019
The diagnosis of bilateral angle-closure
glaucoma without pupillary block was made.
The patient was treated with 0.1%
betamethasone, 1% atropine, 0.5% timolol
and oral acetazolamide. After consultation
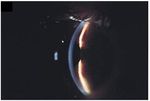
Figure 1. Slit- lamp photograph of the right eye at the
time of presentation, revealing shallowing of the anterior
with the patient's neurologist, topiramate was
chamber stopped and oral acetazolamide was tapered.
Figure 2. Appositional closure of the anterior chamber
Figure 4–A. B-scan ultrasound of the right eye at the
angle
time of presentation, showing ciliochoroidal effusion
Figure 3. Ultrasound biomicroscopy of the right eye
obtained at initial examination showing ciliary body Figure 4–B. Resolution of cilichoroidal effusion two
swelling (CB), ciliochoroidal effusion (*), and a closed weeks after cessation of topiramate
angle (arrow)
One week after presentation, her vision
Pupils were reactive with sluggish response. returned to 20/20 OU. Manifest refraction
Hazy view of the optic nerve revealed normal revealed emmetropia. Slit-lamp examination
cup: disc ratios of 0.3 in both eyes. Ultrasound showed clear corneas and deep anterior
50Topiramate Induced Glaucoma • Sorkhabi et al Iranian Journal of Ophthalmology • Volume 20 • Number 3 • 2008
chambers. Her IOPs were 13 mm Hg OD and physicians should be aware of this adverse
14 mm Hg OS. Gonioscopy revealed open drug reactions.8
angles without synechia in both eyes. Two Rhee et al. described a 43-year-old woman
weeks later the patient's eyes were back to with topiramate associated glaucoma that
normal state and IOP was 15 mm Hg OU included high-frequency ultrasound evidence
without medication. B-scan ultrasound of ciliary process swelling and forward
demonstrated resolution of ciliochoroidal displacement of lens iris diaphragm.6
effusion in both eyes (Figure 4-B). Levy et al. reported a 35-year-old woman
Downloaded from irjo.org at 17:32 +0430 on Monday April 8th 2019
with topiramate-induced bilateral angle-
Discussion closure glaucoma.4
Topiramate is a sulfamate-substituted Craig et al. reported two women, 25 and 45
monosaccharide.4 Several mechanisms elicit years old of age, who developed acute
its antiseizure effect; one of them is weak myopia after starting topiramate. One of them
inhibition of carbonic anhydrase enzyme.5 also developed bilateral angle-closure
The following side effects have been glaucoma.9
reported with topiramate therapy: abnormal The majority of reported adverse events
vision, acute secondary angle-closure have occurred in female patients (up to 89%)10
glaucoma, acute myopia and suprachoroidal which is also the case for the patient
effusions.2 presented in this paper.
Although controversies exists regarding the Management of topiramate-related acute
exact mechanism of acute myopia and angle- pressure elevation requires cessation of the
closure glaucoma after sulfonamide usage, drug after consultation with the prescribing
most authors have attributed this to ciliary physician because decreasing the dose by 50
body swelling.6 mg per dose might exacerbate the preexisting
The pathophysiology of the ciliary body systemic condition.11
swelling is unknown. Krieg and Schipper Topical cycloplegic agents probably lower
noted that repeated use of the same drug the intraocular pressure by retracting the
produces a hypersensitivity reaction. They ciliary processes, along with topical β–
speculate that the drug-induced elevated blockers and oral pressure-lowering agents.12
prostaglandins contribute to formation of Because the mechanism of angle-closure
edema within the ciliary body without any does not involve pupillary block, pilocarpine
evidence of a systemic allergic response.7 and peripheral iridectomy are usually
In addition, topiramat's weak inhibition of ineffective.13
carbonic anhydrase or an effect mediated by
prostaglandin has also been suggested as Conclusion
causative mechanism by some authors.6 Topiramate can cause acute bilateral angle-
Banta et al. first reported a case of uveal closure glaucoma with ciliary body edema and
effusion and secondary angle-closure ciliochoroidal detachment. Physicians should
glaucoma associated with topiramate usage in be aware of the possible ocular side effects
July 2001.3 In September 2001, Ortho-Mc Neil after initiating topiramate use, principally
Pharmaceuticals sent out a “Dear Healthcare during the first 2 weeks. It is also important to
Professional” letter, indicating that 21 cases of advise the patients about the possibility of
acute angle-closure glaucoma had been blurred vision, eye pain, or headache and the
reported to their safety division, and need to seek immediate ophthalmic
investigation in these events.
References
1. Medeiros FA, Zhang XY, Bernd AS, Weinreb RN. Angle-closure glaucoma associated with
ciliary body detachment in patients using topiramate. Arch ophthalmol 2003; 121:282-5.
2. Fraunfelder FW, Fraunfelder FT, Edwin U. Topiramate-associated acute bilateral secondary
angle-closure glaucoma. Ophthalmology 2004; 111:109-11.
51Topiramate Induced Glaucoma • Sorkhabi et al Iranian Journal of Ophthalmology • Volume 20 • Number 3 • 2008
3. Banta JT, Hoffman K, Budenz EL, et al. Presumed topiramate induced bilateral acute angle-
closure glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 2001; 132:112-4.
4. Levy J, Yagev R, Petrova A, Lifshitz T. Topiramate-induced bilateral angle-closure glaucoma.
Can J ophthalmol 2006; 41:221-5.
5. Roff Hilton EJ, Hosking SL, Betts T. The effect of antiepileptic drugs on visual performance.
Seizure 2004; 13:113-28.
6. Rhee DJ, Goldherg MG, Parrish RK. Bilateral angle-closure glaucoma and ciliary body
swelling from Topiramate. Arch Ophthalmol 2001; 119:1721-3.
Downloaded from irjo.org at 17:32 +0430 on Monday April 8th 2019
7. Krieg PH, Schipper I. Drug induced ciliary body edema: a new theory. Eye 1996; 10:121-3.
8. Hulihan J. Important drug warning. Available at
http://www.fda.gov/needwatch/SAFETY/2001/Topamax_deardoc.PDF.AccessedApril17.2003 .
9. Craig JE, Ong TJ, lovis DL, Wells JM. Mechanism of topiramate- induced acute-onset myopia
and angle-closure glaucoma. Am J ophtalmol 2004;137:193-5
10. Thambi L, kapcala LP, Chambers w, et. At. Topiramate- associated secondary angle-closure
glaucoma: a case series. Arch ophthalmol 2002; 120:1108.
11. Fraunfelder FW, Fraunfelder FT. Adverse ocular drug reactions recently identified by the
National Registry of Drug-Induced Ocular side effects. Ophthalmology 2004; 111:1275-9.
12. Sankar PS, Pasquale LR, Grosskreutz CL. Uveal effusion and secondary angle-closure
glaucoma associated with topiramate use. Arch Ophthulmol 2001;119:1210-1
13. Rajol P, Shefali P, Sangamitra D, Ravi T. Choroidul drainage in the management of acute
angle-closure after topiramate toxicity. J of Glaucoma 2007; 16:691-3.
52You can also read