Adaptive User Profiling in E-Commerce and Administration of Public Services
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
future internet
Article
Adaptive User Profiling in E-Commerce and Administration of
Public Services
Kleanthis G. Gatziolis, Nikolaos D. Tselikas and Ioannis D. Moscholios *
Department of Informatics and Telecommunications, University of Peloponnese, 221 00 Tripoli, Greece;
kgatziol@uop.gr (K.G.G.); ntsel@uop.gr (N.D.T.)
* Correspondence: idm@uop.gr
Abstract: The World Wide Web is evolving rapidly, and the Internet is now accessible to millions
of users, providing them with the means to access a wealth of information, entertainment and
e-commerce opportunities. Web browsing is largely impersonal and anonymous, and because of
the large population that uses it, it is difficult to separate and categorize users according to their
preferences. One solution to this problem is to create a web-platform that acts as a middleware
between end users and the web, in order to analyze the data that is available to them. The method by
which user information is collected and sorted according to preference is called ‘user profiling‘. These
profiles could be enriched using neural networks. In this article, we present our implementation
of an online profiling mechanism in a virtual e-shop and how neural networks could be used to
predict the characteristics of new users. The major contribution of this article is to outline the way
our online profiles could be beneficial both to customers and stores. When shopping at a traditional
physical store, real time targeted “personalized” advertisements can be delivered directly to the
mobile devices of consumers while they are walking around the stores next to specific products,
which match their buying habits.
Keywords: user profiling; e-commerce; retailing; e-shopping; mobile shopping; analytics; neural
Citation: Gatziolis, K.G.; Tselikas,
networks; public e-governance
N.D.; Moscholios, I.D. Adaptive User
Profiling in E-Commerce and
Administration of Public Services.
Future Internet 2022, 14, 144. https://
doi.org/10.3390/fi14050144
1. Introduction
The Internet today is a technological and social phenomenon. It affects everyone’s
Academic Editors: Incheon Paik and
daily life and has had significant social impacts. Huge amounts of data and information
B. T. G. Samantha Kumara
are being uploaded to the internet every day. Businesses want to maximize their profits
Received: 6 April 2022 by advertising their services or products to targeted customers, while Internet users want
Accepted: 4 May 2022 to avoid receiving irrelevant information from Internet search results. It is necessary to
Published: 9 May 2022 predict users’ needs to improve their browsing experience and provide them with valuable
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral data. The solution to both problems described above is web personalization via user
with regard to jurisdictional claims in profiling [1–3].
published maps and institutional affil- A User Profile is a group of items and/or patterns used to describe the user briefly.
iations. User Profiling is an especially critical procedure for e-business systems that captures
online users’ attributes, knows online users, provides tailor-made goods and services, and
therefore improves user satisfaction.
To conduct our research, we contacted the major superstores in Greece, asking for
Copyright: © 2022 by the authors. information on the way they have created their online user profiles. Our results show
Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. that while stores do allow users to register and create new profiles, there are times when
This article is an open access article customers provide false data. This problem can occur when no online verification process
distributed under the terms and
is in place. So, a question we must investigate is: which registered customers are supplying
conditions of the Creative Commons
accurate online information?
Attribution (CC BY) license (https://
“User profiling techniques have widely been applied in various e-business appli-
creativecommons.org/licenses/by/
cations, e.g., online customer segmentation, web user identification, adaptive web site,
4.0/).
Future Internet 2022, 14, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14050144 https://www.mdpi.com/journal/futureinternetFuture Internet 2022, 14, 144 2 of 24
fraud/intrusion detection, personalization, e-market analysis, recommendation, as well as
personalized information retrieval and filtering” [4].
User Profiling can be defined as the course of pinpointing the data about a user interest
domain [5,6]. This data can be used by the system to grasp more about the user and be
further utilized to better meet the user’s needs.
In this article, we propose the implementation of an online profiling mechanism in
a virtual e-shop, its success rates, and how neural networks could be used to predict the
characteristics of new users. We also indicate the way our online profiles could be of benefit
both to customers and stores through real time “personalized” advertisements targeted
at customers shopping in physical stores. The proposal of this article is significant since
it could redefine the way we shop at physical stores. If the real online profiles of the
consumers are known, then we could use them to promote in real time, specific products
to certain customers while shopping. A lot of research has already been conducted both
on the techniques of user profiling in online shops and the techniques of user profiling
in physical shopping, so the main objective of this article is to fill in this research gap by
joining these approaches in order to increase the profits of businesses and the affordability
for customers through personalized price offers.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews some related work
and introduces the theoretical basis. Section 3 describes our proposed model, and Section 4
describes the experimental setup as well as the results. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Related Work
2.1. User Profiling
A user profile is a visual representation of the personal data associated with a par-
ticular user, or a customized interface [7]. That is, a profile is the digital representation
of an individual’s identity. However, it can also be considered as the representation of
a user model.
A profile stores the description and characteristics of the individual it represents.
These facts can be utilized by various systems that take into account people’s attributes
and preferences. This is why profiles are essential for a modern system, as the information
found in the profile is personalized, thus enabling us to distinguish and group them.
There are two phases which allow us to acquire the user profile. In the first phase, the
user is asked explicitly to insert his/her initial profile as a goal. He/she can also amend the
profile by hand. Users may not be able to enumerate all their interests at once. So, their
browsing history is used to update their profile. The second phase (user profile acquisition)
monitors the browsing behavior of the user, and through the scheme of content analysis,
the data of the user’s interest are successively acquired.
The information contained in a profile can be either dynamic or static. In the first case,
the profile is called dynamic, and this means that the information can change over time [8,9].
These changes usually occur depending on the actions that the user takes in the system and
usually they cannot use or make changes to this information. In contrast, in the second case,
where the profile is called static, the information in the profile remains constant for a long
period of time and it rarely changes [8,9]. Such a profile will contain mainly demographic
notes about the user, such as name, age, height, etc. In many systems, a combination of the
advantages of static and dynamic can be observed, thus making the profile hybrid [5,10].
Profiles can be found in operating systems, computer programs, recommendation systems,
computer games, etc. [11].
2.2. Profile Structure
According to the previous description referring to the characteristics of the user’s
profile, we can divide the profile into subcategories, namely, the basic and the extended
profile, respectively [12]. The virtual identity is the first thing that the user selects, and it
refers to the user’s ID. This identity is permanent and does not change, whereas it is the
user’s choice whether he wants a pseudonym or his real identity. The basic profile is theFuture Internet 2022, 14, 144 3 of 24
one containing the user’s very basic information (demographic data) and can usually be
altered, although rarely, in accordance with the user’s needs.
The extended profile contains information that changes over time and is not specified
when the profile is created. The information can be changed, or new information can be
entered, making the profile dynamic. Interaction with third-party profiles and policies
requires settings related to data security and user privacy as to who can use this information.
As all these features form the structure of an integrated profile, there are also different
profile design patterns or often a mixture of these patterns.
Static models are the basic types of user profiles. In them, the main data are collected
and will not change again, i.e., they are static. Changes in the user’s choices are not
registered in the system and no algorithms are used to parameterize the profile.
Dynamic models allow a more up-to-date representation of users. Changes are often
made to them over time and through the user’s interaction with the system. These profiles
are particularly useful in adaptive hypermedia as they are updated to take into account the
current needs and goals of the user.
Hybrid models are those that combine static and dynamic models according to the
needs of the system.
2.2.1. Profile Monitoring
In order to analyze a profile, it must first be extensively monitored and all the user’s
actions over time must be recorded [13]. Monitoring a profile consists of three processes:
- Direct monitoring of the use of the application by keeping a history of the usage pattern.
- Storing the history by the system to avoid failures.
- Immediate feedback on the performance of the service.
Of course, this information is particularly valuable, as the risk of user privacy vio-
lation is high, and therefore, this matter raises ethical and legal issues regarding privacy
monitoring [14].
2.2.2. Data Collection
After having created a user profile, the next step is to collect information about the
user so that it can eventually be analyzed. There are several ways to collect information
about users, with some of them discussed below [15].
The easiest and quickest way to collect information is through direct user interaction
with the system, where the latter is asked to answer a series of questions that will help the
system “learn” about him/her. This process usually takes place during registration with
the system, at which point the user is asked to fill in forms or other interfaces that serve
this purpose. Usually, this is an optional type of intelligence as users may not be willing
to fill out lengthy forms, and this information rarely changes over time. In general, this
information is comprised of demographic details, such as the user’s age, marital status
or sex.
However, there are several problems with collecting information in the first way, as
users may not want to provide much data, and this has led to the creation of a second way
which learns the user’s preferences by observing the user interacting with the system. In
this case, the system does not automatically request information about preferences from
the user. Instead, it comes as the user navigates through the system and is subconsciously
asked to make some decisions. Thus, the system learns dynamically from observing their
interactions. For this reason, for the system to learn about a profile, the user’s behavior
should be repetitive, i.e., the user’s actions should be performed under similar conditions
at different points in time.
There is also a third hybrid mode which is a combination of the two above [16,17].
That is, data are collected not only by asking the user to answer questions directly, but also
during the user’s interaction with the system. This mode combines the advantages of the
two previous ones, thus making it ideal for most profiling systems.Future Internet 2022, 14, 144 4 of 24
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. The first method is usually the
best when data need to be collected quickly, but there are several problems. First, it lacks
the ability to adapt to changes and user preferences. Secondly, it is highly dependent on
the user’s willingness to provide the information and it is likely to become invalid after
a period of time. Third, users may not write true information on the forms and those
who are willing to provide true information may not know how to express their interests.
However, users have full control over the information collected and it is their decision what
they want to share with the system.
In the second method, the information is gathered by observing the user’s movements
in the system, so it takes more time to gather information, and this information cannot be
changed or seen by the users. Moreover, if there is no repetition in the user’s actions, the
pattern cannot be discovered. However, this information can be easily and automatically
changed so that the system is always aware of and more accurate regarding the user’s
preferences. This could be a simple case of using cookies to store and track visits from
particular users, including the pages and products viewed, or it could be something more
advanced such as eye movements, or even motion detection [18].
Cookies could be used to save some basic information and preferences about users,
such as their individual login information or favorite sports or politics. They could also be
used for personalization issues. As customers are browsing in e-shops and viewing certain
items or parts of a site, cookies could be used to help build targeted ads. Finally, cookies
could be used to track items users previously viewed, allowing the e-shop sites to suggest
similar goods they might like and keep items in shopping carts for future reference.
However, we must keep in mind that cookies have some negative aspects as well.
Many users regularly delete cookies from their browsers. Others will not allow cookies to
be stored on their machines for security reasons. There are some privacy aspects to be taken
into consideration too. Third-party cookies are generated by websites that are different
from the web pages users are currently surfing. This is because they are linked to ads via
that page. An e-shop with 20 banners/advertisements may generate 20 cookies, even if
users never click on those ads. These cookies could let advertisers or analytics companies
track and analyze an individual’s browsing history. Finally, as mentioned in the above
paragraph, we cannot store advanced information in cookies about customers such as eye
movements, or even motion detection. Consequently, it is better and more secure to store
user’s profiling details in a server-recommendation system.
For all the above reasons, we chose for our implemented recommendation system to
use cookies to store only some basic information about users such as their login data, and
we keep all the important details and the analysis of the customers such as parenthood,
gender, interests, etc., in our system.
The hybrid method attempts to combine the advantages of the first two methods by
directly asking users to provide as much information as possible, and then the system,
observing their interaction, adjusts the user’s profile according to their preferences. In
Table 1, a comparative list of profile types in relation to the researched literature is presented.Future Internet 2022, 14, 144 5 of 24
Table 1. A comparative table of user profile types, in relation to the researched literature.
User Profile Type Description Advantages Disadvantages
Users may not want to provide
much data.
Data are collected quickly. It lacks the ability to adapt to changes
Data gathered are of high quality. and user preferences.
Direct user interaction with Usually, users enter real It is highly dependent on the user’s
Explicit user the system. information when they enroll. willingness to provide
profile Users manually create and fill Users have full control over the the information.
in main data. information collected. Users may not write true information
Users decide what they want to on the forms.
share with the system. Users who are willing to provide true
information may not know how to
express their interests.
It takes more time to gather valuable
User’s information can be easily
information about users.
and automatically updated so that
The system learns If there is no repetition in the user’s
Implicit user the system is always aware and
dynamically from observing actions the pattern cannot
profile more accurate about
user interactions. be discovered.
their preferences.
The information cannot be changed
Minimal user effort is required.
or seen by the users.
Combine the previous
methods and adjust the user’s
Hybrid user profile Advantages of both techniques. Disadvantages of both techniques.
profile according to
their preferences.
2.2.3. Data Analysis
Data analysis is a process for inspecting, cleaning, transforming and modeling data in
order to discover information that is useful for decision making by users. Data analysis can
be distinguished into several phases as shown below [19].
Data collection as presented is next to the requirements that are determined based on
those that guide data analysis.
Data processing includes the phases where raw information is processed and converted
into information which is ready to be analyzed. This may involve entering data into rows
and columns in a tabular format, such as a spreadsheet or database.
Data modeling is the process wherein mathematical formulas or algorithms are applied
to the data to display the relationships between variables so that the information can be
ultimately visualized to be understood by the user.
However, all of the above depends on the initial phase of data analysis which consists
of four questions. These questions have to do with the quality of the data, the quality of
the measurements, data transformation and whether the collected information meets the
requirements of the survey design [20].
2.3. User Modeling
User modeling is a part of human–computer interaction and describes the process
of creating and modifying a user model [21]. The main goal of user modeling is to adapt
systems to the specific needs of the user. The system must appear to be built for each
individual user, while it is built for hundreds of millions of users. That is, it should say
“the right thing, at the right time, in the right way” [22].
User modeling consists of two main categories. The first is the user model, which is
the set of information that makes up the user profile, and the second is data collection. The
set of information that makes up the profile is all the data that make the profile distinct
from the rest. Data collection is also a separate chapter in itself, as through it we can extend
the information we have about a user either by asking the user to provide it or by trackingFuture Internet 2022, 14, 144 6 of 24
the user’s actions in the system. The latter is extremely important for a system that can
adapt to the user’s needs [23].
A very simple example of user modeling is e-commerce websites that use all the
information about a user’s browsing and shopping and combine it with information from
other users in order to better understand their shopping preferences. Thus, the system can
easily suggest possible products that may be of interest to users.
Types of Data in User Models
User data includes data about users’ interaction with the system [24]. Thus, each user
is made according to this data and is made to stand out from the rest. The following are the
types of data that can be incorporated into user models.
Demographic data has information about the first name, last name, age, height, weight,
gender, nationality, place of residence, etc. These data can be expanded and modified to
a huge extent depending on the requirements of the application. Usually, they form the
static part of the profiles as this information changes very rarely to never. By looking at
these elements, we can group the users of the system according to their profile and look at
their actions individually. This, again, could be useful in an e-shop system as, for example,
we could look at the shopping preferences of the two genders separately.
Knowledge or background data is perhaps one of the most important in user models.
These data are usually not subject to frequent changes, and they are determined in the short
term, thus forcing systems to be dynamic. This means that the system should understand
the changes in knowledge acquired by the user by observing the user’s movement and
choices in the system and adjust the data to make it more useful to the user.
Interest and preference data are the most important pieces of information in systems
that filter information, such as recommendation systems. However, it is usually different
from demographic information, as the user does not need to be asked about it. Instead, by
observing the recurring patterns in users’ actions, an ideal system could infer the user’s
interests on its own.
The user’s individual traits are the set of user characteristics (extrovert, reactive, etc.)
that are not subject to any change or that change over a long period of time. That is
why many such systems with this kind of information can be static. Examples of such
systems are specially designed psychological tests. As before, this information differs from
demographic information, as here too it is particularly important to observe recurring
patterns in the actions of users.
2.4. Uses of User Model Data
We have analyzed the profiles and the information that populates them. A modern
profile should have information that has been gathered either dynamically or statically and
this information should form a personalized profile of the user. Once a system has gathered
information about users, it can begin to present the data or even use it to its advantage.
Profiling can be used, with many important benefits, in several applications, some of which
are presented below.
2.4.1. Experienced Systems
Experiential systems are computer systems that can mimic human decision-making to
help solve a problem in a particular area. These systems work by asking questions step
by step to pin down the issues that come up and find solutions [25]. User models can be
used to comply with the user’s current knowledge and differentiate between experienced
and novice users. The system is able to conclude that skillful users are in a better position
to understand more complex queries than someone who is new to the domain. Thus, it
adapts its vocabulary and the queries it uses to find a solution.by step to pin down the issues that come up and find solutions [25]. User models can be
used to comply with the user’s current knowledge and differentiate between experienced
and novice users. The system is able to conclude that skillful users are in a better position
to understand more complex queries than someone who is new to the domain. Thus, it
Future Internet 2022, 14, 144 adapts its vocabulary and the queries it uses to find a solution. 7 of 24
2.4.2. Recommendation Systems
2.4.2. Recommendation
Recommendationsystems Systemsare application tools and techniques that give suggestions
for objects that a user might
Recommendation systems want
are to use. These
application recommendations
tools and techniques may be decisions
that give that
suggestions
the user wants to make, such as: which is the best purchase, what
for objects that a user might want to use. These recommendations may be decisions that kind of music he/she
would
the userlike
wantsto listen
to make,to, orsuch
whatas:news whichto read
is the[26].
best purchase, what kind of music he/she
would like to listen to, or what news to read of
The basic idea is to present a selection items that best fits the user’s needs, which
[26].
are determined based on analysis of
The basic idea is to present a selection of items the user’s profile
that during
best fitsprofile creation
the user’s needs,orwhich
while
navigating
are determined the application.
based on analysis of the user’s profile during profile creation or while
Recommendation
navigating the application. systems have become prevalent nowadays and are widely used in
a variety of applications.
Recommendation systems The mosthave popular applications
become prevalent are probably
nowadays and are movies,
widelymusic,
used
news, books, research articles, search engine queries, products,
in a variety of applications. The most popular applications are probably movies, etc. A typical example of
music,
a recommendation system is the www.stumbleupon.com (accessed
news, books, research articles, search engine queries, products, etc. A typical example of on 5 April 2022)
awebsite system, which
recommendation system uses
is thethewww.stumbleupon.com
web ratings gathered (accessed
by a collaborative
on 5 April rating system
2022) website
that canwhich
system, match usesusersthe withwebinteresting websites by
ratings gathered based on their preferences.
a collaborative rating system that can
matchFor example,
users for two users
with interesting with based
websites the same preferences,
on their a recommendation system is
preferences.
capable
For of suggesting
example, something
for two users with that the
maysamebe ofpreferences,
interest to the second user, depending
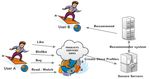
a recommendation system on
is
the data provided from the first one. Figure 1 shows two people
capable of suggesting something that may be of interest to the second user, depending on with the same prefer-
ences
the data(they look almost
provided from the the same,
first one. they
Figurehave similar
1 shows two ages, theywith
people aretheof the
same same gender,
preferences
they probably
(they look almost likethe similar
same,clothes)
they have andsimilar
how aages,
recommendation
they are of the system
same is capable
gender, of
they
probably
suggesting like similar clothes)
something that may andbe how a recommendation
of interest to User B basedsystemon isthe
capable of suggesting
data provided from
something
User A. that may be of interest to User B based on the data provided from User A.
Figure1.
Figure 1. Recommendation
Recommendation system.
system.
2.4.3.
2.4.3. User
User Simulation
Simulation
Since
Since modelinga auser
modeling lets
user thethe
lets system
systemperform an internal
perform representation
an internal of a particular
representation of a par-
user, user
ticular simulation
user, allows us
user simulation to perform
allows usabilityusability
us to perform testing. These
testing.tests involve
These tests ainvolve
processa
used
process used to evaluate a product by testing it on these users, thereby providingidea
to evaluate a product by testing it on these users, thereby providing the basic the
of howidea
basic realofusers
how would use would
real users the system,
use theand the tests
system, andfocus on measuring
the tests the abilitythe
focus on measuring of
aability
product to satisfy someone [27]. A few striking examples of goods that profit
of a product to satisfy someone [27]. A few striking examples of goods that profit from these
tests
fromare websites,
these food,
tests are consumer
websites, food,products,
consumer computer
products,interfaces,
computeretc. interfaces, etc.
2.5. Knowledge Extraction
Knowledge mining in Computer Science (also called knowledge discovery in databases),
is the process of detecting interesting and useful patterns and pertinence in great numbers
of data [28]. The field of knowledge mining combines artificial intelligence tools and
techniques with database management and is widely used by businesses (insurance, bank-
ing, etc.), in scientific research (medicine, physics etc.) and in government security systems
(criminality and terrorism actions). Thus, using clustering or categorization algorithms,
data are extracted to help humans make appropriate decisions.gorithms, data are extracted to help humans make appropriate decisions.
Companies’ transactional data have significantly increased; thus, the deman
more sophisticated systems capable of discovering the knowledge contained withi
data has come to the foreground. A successful application of data mining was the
Future Internet 2022, 14, 144 8 of 24
tion of credit card fraud. The system studied the consumer’s buying behavior an
played a pattern for them. Any purchase made outside this pattern led to an inve
tion. Companies’ transactional data have significantly increased; thus, the demand for more
The complete
sophisticated systemsdata mining
capable processtheinvolves
of discovering knowledge multiple
containedstages,
within thatwhich are inform
data has
gathering
come to theand pre-processing,
foreground. A successfulinapplication
which, before the data
of data mining wasmining algorithms
the detection of credit are ap
card fraud. The system studied the consumer’s buying behavior
the surveyed set of information is assembled. Then, the data are processed, and displayed a pattern which en
for them. Any purchase made outside this pattern led to an investigation.
data mining and results in the interpretation of the database. To achieve the afor
The complete data mining process involves multiple stages, which are information
tioned process,
gathering there are some
and pre-processing, techniques
in which, before thewhich are discussed
data mining algorithms below.
are applied, the
Predictive
surveyed modelingis is
set of information used when
assembled. Then, we aimare
the data atprocessed,
estimating which the valuedata
enables of a part
miningand
feature and results
we know in thesome
interpretation of the database.
of the values To achieveAn
of the attribute. the aforementioned
example is data clas
process,
tion, whichthere are somea techniques
gathers group of which are discussed
data that have been below.sorted into predefined sets and
Predictive modeling is used when we aim at estimating the value of a particular
for patterns
feature and we inknow
the some
data ofthat differentiate
the values these An
of the attribute. groups.
exampleThese
is datadiscovered
classification, pattern
then
whichbegathers
reuseda to classify
group other
of data data been
that have when the name
sorted for the group
into predefined sets andattribute
looks for is unkn
For example,
patterns in theadata
manufacturer maythese
that differentiate develop
groups.predictive modelspatterns
These discovered to distinguish
can then which
be reused to classify other data when
fail in extremely hot or cold temperatures. the name for the group attribute is unknown. For
example, a manufacturer may develop predictive models to distinguish which parts fail in
A second technique is descriptive modeling or clustering, which also subdivid
extremely hot or cold temperatures.
items A into groups.
second Withisarraying,
technique descriptivethe appropriate
modeling sets may
or clustering, whichnotalsobe known in
subdivides its advanc
they
itemsare discovered
into groups. With after analysis
arraying, of the data.
the appropriate setsFor
mayinstance,
not be knownan advertiser
in advance, but may inter
they are discovered after analysis of the data. For instance, an advertiser
general population in order to categorize plausible consumers into many kinds of g may interpret
a general population in order to categorize plausible consumers into many kinds of groups
and then develop separate advertising campaigns [28]. Figure 2 shows the clusterin
and then develop separate advertising campaigns [28]. Figure 2 shows the clustering
groups.
into groups.
Figure 2. Clustering.
Figure 2. Clustering.
The next data mining technique worth mentioning is pattern mining. This technique
focuses on establishing modes that present specific patterns within the data. They are often
The next data mining technique worth mentioning is pattern mining. This tech
used in stores trying to find out which products are commonly purchased along with some
focuses on Although
other ones. establishing modes
testing that present
such insights specific
is possible withoutpatterns
the help ofwithin the data. The
an application,
often used in
data mining hasstores trying
facilitated to find out
the discovery which products
of associations are commonly
in less obvious purchased
datasets. Figure 3
with someinother
illustrates ones.
a simple wayAlthough testing
how the pattern such
mining insights
technique is possible
is used without the help
in the data.
application, data mining has facilitated the discovery of associations in less obvioFuture Internet 2022, 14, x FOR PEER REVIEW 9 of 25
Future Internet 2022, 14, 144 9 of 24
tasets. Figure 3 illustrates in a simple way how the pattern mining technique is used in
the data.
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Pattern MiningAvailable
Pattern Mining Availableonline:
online:https://borgelt.net/teach/fpm/
https://borgelt.net/teach/fpm/ (accessed
(accessed on
on 55 April
April 2022).
2022).
2.6. Similar Systems
2.6.1. The WEST
2.6.1. The WEST System
System
When
When analyzing
analyzing user user analysis
analysis systems,
systems, it it is
is important
important to to refer
refer to
to early
early systems
systems that
that
became pioneers in their field. One of these was the WEST
became pioneers in their field. One of these was the WEST system [22]. system [22].
The
The WEST
WESTsystemsystemwas wasa tutorial forfor
a tutorial a game called
a game HowTheWestWasWon.
called HowTheWestWasWon. In thisIn
game,
this
players spin three spinners and have to create numerical expressions
game, players spin three spinners and have to create numerical expressions with the with the numbers
spin,
numbersusing +, −using
spin, , ×, / +,and−, appropriate parentheses
×, / and appropriate to determine
parentheses what the final
to determine whatvalue will
the final
be. So, if, for example, the player rolled 2, 3 and 4 with the spinners, they could create
value will be. So, if, for example, the player rolled 2, 3 and 4 with the spinners, they could
the numerical expression (2 + 3) × 4 = 20 and advance 20 places. If a player reaches one
create the numerical expression (2 + 3) × 4 = 20 and advance 20 places. If a player reaches
city (i.e., every 10 places), he automatically advances to the next city, and if he lands on
one city (i.e., every 10 places), he automatically advances to the next city, and if he lands
an opponent, then he is sent back two cities. Thus, it makes it an optimal strategy for the
on an opponent, then he is sent back two cities. Thus, it makes it an optimal strategy for
user to have to calculate all possible moves that put him ahead of his opponents. By thus
the user to have to calculate all possible moves that put him ahead of his opponents. By
analyzing the players’ moves, the system discovered that the most popular strategy was to
thus analyzing the players’ moves, the system discovered that the most popular strategy
add the two smallest numbers and multiply them by the largest.
was to add the two smallest numbers and multiply them by the largest.
Although the WEST system explored some of the basic concepts of user modeling,
Although the WEST system explored some of the basic concepts of user modeling,
due to the limited results, it worked very well by analyzing player behaviors so that they
due to the limited results, it worked very well by analyzing player behaviors so that they
could be understood by users.
could be understood by users.
2.6.2. The Gumsaws System
2.6.2. The Gumsaws System
The Gumsaws system was created to support the construction of adaptive web
pagesThe[29].Gumsaws
This systemsystem waswas ablecreated
to meettothe support the construction
scalability, replaceability of and
adaptive web
adaptabil-
pages
ity [29].
needs of aThis system
website was able users.
by modeling to meet the this
It did scalability,
by usingreplaceability and adaptability
knowledge mining techniques
needs
to learnofthe
a website by modeling
user’s navigation users. It did this by using knowledge mining techniques
history.
to learn the user’s navigation history.
The Gumsaws system had features to create a profile or group of profiles and to store,
The update
retrieve, Gumsaws and system had features
delete entries. These to create awere
functions profile or group
performed byofthe
profiles
systemand to
using
store, retrieve,
various sourcesupdate and delete
of information, entries.
such These
as direct functionswhich
information were performed
came directlyby from
the system
users,
using various
group information sources
which of came
information, suchnavigation
from users’ as direct information which camebetween
history and correlations directly
from users,
them. Thus, group information
the system could bewhichused bycame
news from users’and
systems navigation
served itshistory and correla-
users according to
tions preferences.
their between them. Thus, the system could be used by news systems and served its us-
ers according to their preferences.
2.6.3. The CATS System
The Collaborative Advisory Travel System (CATS) was recommended as a solution to
suggest a plan for ski holidays for a group of friends [30]. This allowed a group of users
to work together at the same time in order to choose a ski vacation package that satisfiedFuture Internet 2022, 14, 144 10 of 24
the whole group. The system revolved around the interactive DiamondTouch tabletop that
allowed developing group recommendations that can be shared virtually among up to four
users. The proposals relied on a group profile which was a mix of personal inclinations.
2.6.4. The PCAHTRS System
The PCAHTRS system is a Personalized Context-Aware Hybrid Travel Recommender
System proposed by R. Logesh and V. Subramaniyaswamy [31]. With this system, they
tried to propose a way to achieve better personalized recommendations in the e-tourism
domain. The main purpose of this model was to design a hybrid collaborative filtering
travel recommender system that provides personalized tourist venues based on ratings
and desires. It is shown that the form of the implicit and explicit preferences of users
extended with the semantic models is the key to uncertainty issues that come up in the
recommendation process. PCAHTRS was based on the user contextual information and
opinion mining technique to improve accuracy in prediction.
2.6.5. The Hootle
Hootle was a group recommender system (GRS) proposed by JO Álvarez Márquez
and J Ziegler [32]. In this system, user preferences and needs were modified in group
discussions and users could interact with the desired features of the items. All group
members should therefore accept or reject the proposed features and manage group choices
according to their importance.
3. Our Proposed Implementation
Artificial intelligence is radically changing our lives and has been around for a long
time. Through the COVID-19 pandemic, it has been given a new impetus, since public and
private lives are now largely played out online. Any registration system primarily aims at
collecting information on site visitors, not only to determine who is coming to the site, but
also to facilitate informed decisions concerning the site design and content.
Marketers pay critical attention to customer profile data, which are used to better
understand their audience, how they use the website, what products they like, their offline
interests, and who is on their social media. The value of the database depends on the quality
of the data it contains, and 88% of customers admit that traditional registration forms
provide incomplete or incorrect information, so the database does not contain the required
quality of data. Poor data quality can result in lost sales, ineffective direct marketing,
administrative costs and a loss of 10–20% of annual revenue in avoidable distribution
errors [33].
Users need a platform that checks and verifies data provided upon signing up. This
will boost the profitability of the business and give consumers a sense of uniqueness
by receiving targeted advertising—discounts—and recommended products on the site’s
specially designed “personal” page. Generally, users who are already registered do not
meddle with updating their profile, since they have already received access to the platform.
Additionally, many users who are concerned about their personal information do not
include their real personal data online. They intentionally (in most cases) give incorrect
information. These fake profiles can be modified or updated with more data using the
methods for unregistered users. Given the above, we created a “user profile extraction
engine” called Profiler for a virtual web shop. Through this implementation, we can track
users’ movements and create their profiles accordingly. Our primary goal was to create
and edit a profile for e-commerce purposes.
3.1. The Database
The database is used for the static data of the users entered during registration,
the dynamic data entered during their navigation and for the products. The database
consists of four tables: members (users), products (products), tracking (tracking) and item
bought (purchases).3.1. The Database
The database is used for the static data of the users entered during registration, the
Future Internet 2022, 14, 144
dynamic data entered during their navigation and for the products. The database consists 11 of 24
of four tables: members (users), products (products), tracking (tracking) and item bought
(purchases).
The users table consists of only three elements: the username, password and an ID
The user.
for each usersThis
tableIDconsists of only
is unique three
for each elements:
user thekey
and is the username, password
that connects and an
this table ID
to the
for each user.
tracking table.This ID is unique for each user and is the key that connects this table to the
tracking table.
The tracking table contains data that attempt to determine whether the user is male
The tracking table contains data that attempt to determine whether the user is male
or female, whether they have children and what their hobbies are. It also keeps a record
or female, whether they have children and what their hobbies are. It also keeps a record
of when they last logged in, how many times they have shopped at the store, how much
of when they last logged in, how many times they have shopped at the store, how much
money they have spent and other personal information, if any.
money they have spent and other personal information, if any.
The product table contains one-by-one information and images of the products as
The product table contains one-by-one information and images of the products as well
well as information that helps the system to categorize the products and answer the
as information that helps the system to categorize the products and answer the queries
queries received from the user during the shopping process.
received from the user during the shopping process.
Finally, the shopping table (items bought) contains information about the purchases
Finally, the shopping table (items bought) contains information about the purchases
made by each user. Figure 4 shows the tables and some of the elements and keys that
made by each user. Figure 4 shows the tables and some of the elements and keys that make
make up the system’s database.
up the system’s database.
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Database tables.
tables.
3.2.
3.2. User
User Tracking
Tracking Technique
Technique
The
The process of user
process of user tracking
tracking is
is also
also the
the point
point where
where profiles
profiles are
are dynamically ‘built’.
dynamically ‘built’.
Every time a user makes a query in the database, the database displays the appropriate
Every time a user makes a query in the database, the database displays the appropriate
products and at the same time notes, by editing the user’s profile, the categories of interest.
products and at the same time notes, by editing the user’s profile, the categories of in-
PHP was used for server-side scripting and database communication. The dynamic
terest.
editing of the profile is not visible to the ordinary user but only to the administrator of the
PHP was used for server-side scripting and database communication. The dynamic
website and cannot be edited unless the information in the database is ‘tampered with’.
editing of the profile is not visible to the ordinary user but only to the administrator of the
We mentioned in Section 2.2.1 the ways in which it is possible to monitor profiles.
website and cannot be edited unless the information in the database is ‘tampered with’.
In this application, the ideal way is the second one, i.e., monitoring through the user’s
We mentioned in Section 2.2.1 the ways in which it is possible to monitor profiles. In
actions. In this way, by observing the recurring patterns of users, the system can adapt
this application, the ideal way is the second one, i.e., monitoring through the user’s ac-
to changes in the user’s interests, likes, routines and targets. The only downside is that
tions. In this way, by observing the recurring patterns of users, the system can adapt to
“building” a complete profile can take some time, and if not given enough time to create
changes
some in the patterns
recurring user’s interests, likes,
by the user, theroutines
data mayand targets.
appear The only downside is that
incomplete.
“building” a complete profile
More specifically, the way can take some
a profile time, and
is tracked hasif to
notdogiven
withenough timevisited
the pages to create
in
some recurring patterns by the user, the data may appear incomplete.
the application. That is, if a user visits men’s products very often, the system will know
this and will increase the number of times this user has visited men’s products. All this
information is stored and tracked in our system’s databases and not in cookies for various
reasons as we showed in Section 2.2.2. By observing the user for some time, the system will
have enough information about him/her so that the administrator can distinguish him/her
from the others. Similarly, if users are browsing and constantly searching for products
or information on pages of our online store that contain items for infants or children, ourFuture Internet 2022, 14, 144 12 of 24
system also classifies them as potential parents. Thus, our system creates a profile for each
registered user, constantly updating it with information related to gender, age, and financial
and family status.
3.3. Data Analysis and Display Technique
The final stage is to calculate and display statistics according to the preferences of each
individual user. This option is only visible to the application administrator and allows the
administrator to search for a user. The application, in turn, searches for the user in the
database and all the data that make up the user. It then calculates the data and displays it
so that it can be understood by the administrator. The analysis is the process in which the
system takes the information where the user was looking at men’s, women’s or parent’s
products and their categories and calculates them as percentages according to their choices.
The data are displayed through tables where all the categories are displayed, and the
administrator can clearly see the demographics and interests of the user.
More specifically, as is shown in Figure 5, the system administrator can see detailed
information for each user, such as their username, statistical data on the user’s gender,
his/her likes and much more personal information. For example, the user in this example,
based on his/her statistical analysis, is 10% male and 90% female, so she is probably
a female. There is also a prediction regarding whether this user has or does not have a child.
According to the user’s navigations and the percentage of traffic of each sport activity, the
administrator can see in percentages whether he/she likes running, football, basketball,
gymnastics, tennis, hiking, swimming or cycling. The system administrator also has access
to additional information about each user, such as what date the account was created, when
the user last logged in, how many times he/she has logged in to the online store since
creating the account, how many times he/she has shopped in the store and how much
money he/she has spent in total. The personal details of each user are also presented, for
example, in which city he/she lives, at which address, his/her e-mail address, telephone
number and other address details. Additionally, the administrator can see if there are any
Future Internet 2022, 14, x FOR PEER REVIEW 13 of 25
discount coupons in his/her profile and a table of all the products he/she has bought in
the past. So, the administrator has a complete overview of each user.
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Data
Dataanalysis
analysisand
anddisplay
displaytechnique of aofuser.
technique a user.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Testing of the Application with Real Users, Analysis of the Results through Questionnaires
and SPSSFuture Internet 2022, 14, 144 13 of 24
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Testing of the Application with Real Users, Analysis of the Results through Questionnaires
and SPSS
As mentioned in Section 3, a profiler prototype has been designed and implemented
that takes information and interprets it as logical clusters, which are capable of being
interpreted by humans and other appropriate programs that will monitor them.
The application represents an online store (e-shop) of sporting goods. Users log into
the system and make their purchases. As users navigate through the e-shop, the system
tracks the users’ movements and records them individually. In this way, we are able to
understand some preferences of each user and even some personal data, such as their age,
their gender or even if they are parents.
At the end of the visit of the users or potential buyers of the online shop, the users are
asked to fill in a questionnaire. The questionnaire contains the same questions for all users
and helps us to verify and check the validity of the information and data extracted by the
user analysis system.
4.2. European Data Protection Regulation
The information collected is very personal and there is a risk of violation of the user’s
privacy. There are legal and ethical issues regarding the surveillance of people’s privacy.
The Data Protection Authority, also known as the General Data Protection Regulation
(GDPR), is a constitutionally independent administrative authority. It was established by
a law for the protection of every person from the processing of data concerning personal
data, which incorporates a European Directive into Greek law [34]. This directive sets
certain rules for the protection of personal data in all member countries belonging to the
European Union. In our developed system, we respect and protect the privacy and the
free development of the personality of each user, since this is a primary objective of any
democratic society.
Any electronic application should maintain and establish a level of security and
protection that is on a par with that of existing services, but at the same time capable of
ensuring that personal data is used in a lawful and transparent manner in the interest of
citizens–consumers. Due to the provision of electronic services, citizens who use them
disclose personal data; thus, there is electronic collection and processing of important
information about each citizen, which can be used to create an extensive profile or help
unauthorized persons to access all the information. As Lopes H, Pires IM, Sánchez San Blas
H, García-Ovejero R, Leithard write in their article, “Data privacy has had a vast prominence
in society. Several approaches are taken to realize the dream of one day. There could be a world in
which there is a real state of privacy for the individual” [35].
All online applications of any institution must inspire security during transactions, as it
is vital that citizens/business users have confidence in the systems used by the public. Trust
is consolidated by the existence of appropriate mechanisms for user identification, security
and protection of personal data. Users should be made aware of how their personal data
are protected and how risks arising from malicious actions by third parties are addressed,
such as in cases of hacking of personal data, unauthorized use of services, unauthorized
access to data, etc.
Directly intertwined with the security of Public Websites is their reliability and their
acceptance by visitors–users. They should provide satisfactory security and reliability,
ensuring the following parameters:
- Integrity: which refers to ensuring that the information that is handled, published,
stored and processed remains unchanged.
- Identification: which refers to the identification of the user’s identity;
- Confidentiality: which refers to access to information only by those who have the
appropriate authorization.
- Authentication: refers to the specific action that ensures that the identity declared by
the user actually corresponds to the user.Future Internet 2022, 14, 144 14 of 24
- Authorization: which refers to ensuring that each entity has access to those system
resources to which it has been granted access.
- Availability: relating to the availability of information whenever an authorized user
attempts to access it.
- Non-repudiation: which refers to the inability of a user to deny that he/she has
performed an action related to accessing, entering and processing information. The
security of public websites consists of a complex set of guidelines and rules relating
to the organization of the website operator and the hosting provider, the procedures
it applies, the services it provides, the technical infrastructure at its disposal and,
finally, the legal framework for the protection of personal data and the security
of communications.
Unfortunately, however, the preceding analysis has shown that, from a legal point of
view, there are many different issues that need to be addressed immediately and specifically.
Among the most important issues are undoubtedly those relating to data security and, more
specifically, the issues relating to the authentication of the identity of the communicating
parties, the integrity of the data transmitted, the confidentiality of the data from possible
unwanted disclosure to third parties and the non-derogability of the data.
In order for any public or private agency to proceed with lawful processing of citizens’
personal data, it should, for example, have collected the data in a fair and lawful manner,
for clear and defined purposes, the data should not be more than necessary and should
be accurate and up to date. In conclusion, we must point out that if the challenges are
overcome, Data Security–Legal Aspects will evolve the World Wide Web into a Web with
many new possibilities and will greatly affect many of the activities of our daily lives.
4.3. Statistical Analysis of Data
For the purposes of this article, the statistical program SPSS was used to group,
compare and draw conclusions about the quality and reliability of the information produced
by the user analysis system.
In our sports e-shop, the adaptive profiling system that we created holds information
and analyzes and makes predictions regarding the following categories:
- Hiking
- Swimming
- Running
- Cycling
- Football
- Basketball
- Gym
- Tennis
- Sex (Male or Female?)
- Parent (Is this user a parent?)
Accordingly, variables for the same categories were used for the “real” data provided to
us through the questionnaires. One hundred adults from all educational levels completed
the questionnaires after having made some virtual purchases in our online store. The
questionnaire consists of 11 questions, and provides data about respondents from different
points of view, such as sex, age, interests, parenthood, education, etc. The selection of
these individuals was random. The purpose of this survey was to collect, per user, his/her
personal data and his/her interests and to subsequently compare these data with those
recorded and predicted by our online profiling system. The results of the survey were
very encouraging and showed that our system in most cases worked extremely well.
Detailed examples are presented below. More specifically, the questions they were asked to
answer were:
Question: Which username did you use when you registered?Future Internet 2022, 14, 144 15 of 24
This question was asked to know exactly which username he/she used when he/she
created the account in our system so that we can compare our findings for that specific user.
Question: What is your gender?
According to the replies to the questionnaires, 57 were males and 43 were females. Our
online profiling system successfully predicted the gender for 84 of those users (47 males
and 37 females). This means that the success rate of our system for the gender reached
a percentage of 84%. In Table 2, the success rate of the gender prediction is presented.
Question: Are you a parent?
Of the participants, 32 replied that they were parents and 68 replied that they were not.
Based on the findings of our system, it predicted the correct parenthood for 49 of those
users. In Table 3, the success rate of the Parenthood prediction is presented.
Question: What are your interests? Choose the ones that interest you (Running, Football, Basketball,
Gymnastics, Tennis, Hiking, Swimming, Cycling)
In this question, users had the choice to pick any activities that they really like. For each
one of these activities and for every user, we analyzed the findings of our profiling system.
It turned out that the system worked very well and made accurate predictions. In the
following tables the success rates of each activity is presented.
Table 2. Gender analysis.
Real Data from Profiling System
Gender Success RATE
Questionnaires Accurate Predictions
Male 57 47 82%
Female 43 37 86%
Total 100 84 84%
Table 3. Parenthood analysis.
Real Data from Profiling System
Parent Success Rate
Questionnaires Accurate Predictions
Yes 32 12 37.5%
No 68 37 54.4%
Total 100 49 49%
In Table 4, the success rate of the Running activity prediction is presented.
Table 4. Running activity.
Real Data from Profiling System
Running Success Rate
Questionnaires Accurate Predictions
No 78 63 81%
Yes 22 11 50%
Total 100 74 74% 1
1 The success rate of our system for the running activity is 74%.
In Table 5, the success rate of the Football activity prediction is presented.You can also read